Gate Research: Pullback Driven by Deleveraging | Ethereum and Solana Diverge
Crypto Market Overview
- BTC (-2.48% | Price: 92,639.9 USDT): BTC experienced a rapid deleveraging pullback during its high-level consolidation. After a prior surge, the price entered sideways consolidation, with short-term moving averages (MA5, MA10) flattening and turning down, while the medium-term moving average (MA30) remains relatively stable. Although short-term momentum has cooled, the overall structure remains intact. The break below the lower boundary of the consolidation range triggered stop-losses and liquidations, leading to a sharp drop on the 1-hour chart with a long lower shadow, showing clear support around $92,000. If BTC can hold the $92,000 support, the price action may remain in the $92,000–$96,000 consolidation range. Resistance remains at the $95,000–$96,000 zone for any short-term rebound.
- ETH (-2.78% | Price: 3,200.36 USDT): ETH declined along with BTC, with an overall structure appearing more passive. After rebounding to the $3,350–$3,400 range, the price entered sideways movement. Short-term moving averages (MA5, MA10) flattened and turned downward, while MA30 also leveled off, indicating insufficient internal momentum. Driven by BTC’s drop, ETH broke below the lower boundary of its consolidation range, triggering stop-losses and liquidations. On the 1-hour chart, it quickly dropped to around $3,180 and formed a long lower shadow, suggesting some support in that area. Going forward, the $3,180–$3,200 range is a key support level. If it holds, ETH may continue consolidating between $3,200 and $3,350. Resistance lies at $3,320–$3,350, with stronger pressure around $3,380–$3,400.
- Altcoins: The Fear and Greed Index dropped from 49 to 44 since yesterday, indicating a shift in sentiment from “neutral” toward “fear.” The amplified losses in high-beta altcoins reflect a temporary contraction in risk appetite, with capital exiting more volatile assets first.
- Macro: On January 16, the S&P 500 Index fell by 0.064% to 6,940.01 points; the Dow Jones Index dropped 0.17% to 49,359.33 points; and the Nasdaq Index declined by 0.062% to 23,515.39 points. As of 11:10 AM (UTC+8) on January 19, the spot price of gold is $4,666.17 per ounce, up 1.52% in the past 24 hours.
Trending Tokens
DUSK DUSK Network (+81%, Market Cap: $99.8 Million)
According to Gate market data, the BOT token is currently priced at $0.20, up over 80% in the past 24 hours. Dusk Network (DUSK) is a blockchain platform focused on privacy protection, aiming to provide compliant zero-knowledge proof solutions for financial applications, supporting security tokenization and RWA use cases.
DUSK’s surge is mainly driven by fundamental breakthroughs, combined with capital inflows and market momentum. Recent catalysts include the launch of its mainnet, which boosted market confidence, and integration with Chainlink to enable RWA tokenization. Additionally, a partnership with Dutch licensed exchange NPEX allows for the issuance of securities worth up to €200 million, further promoting institutional adoption. Meanwhile, spot trading volume has surged to several hundred million dollars in the past 24 hours, and open interest in futures has jumped over 80%, indicating significant capital inflows.
NAM Namada (+103%, Market Cap: $3.12 Million)
According to Gate market data, the NAM token is currently priced at $0.00318, up over 100% in the past 24 hours. Namada (NAM) is a Layer 1 blockchain focused on multichain privacy. It uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, supports the IBC protocol, integrates with the Cosmos ecosystem, and provides asset-agnostic privacy protection applicable to cross-chain asset transfers and DeFi applications.
NAM’s surge is mainly driven by technical breakout and capital movement under low liquidity, but lacks strong fundamental support. Some traders noted that NAM broke out of a falling wedge pattern, generating a bullish signal. As a low-cap asset, even small buy orders can push the price up, and the inflow of funds is likely driven by retail FOMO. Overall, there is no significant fundamental news, and the rally appears to be speculative in nature due to NAM’s small market cap.
FRAX Frax (+29%, Market Cap: $104 Million)
According to Gate market data, the FRAX token is currently priced at $1.12, up over 29% in the past 24 hours. Frax (FRAX) is the governance token of Frax Finance, a decentralized stablecoin system known for its partially algorithmic stabilization model. It supports RWA integration and expands DeFi applications through Layer 2 solutions like Fraxtal.
FRAX’s surge is mainly driven by rebranding and ecosystem expansion. The rebranding from FXS to FRAX was completed on January 15, 2026, with adjustments made on major exchanges such as Gate, directly enhancing visibility and liquidity. Recent catalysts include the launch of FraxNet, an account-based platform that supports minting, redemption, and yield generation of frxUSD across 20+ blockchains, enabling self-service access.
Alpha Insights
ETH staking entry queue hits highest level since August 2023, exit queue fully cleared
According to ValidatorQueue data, since the beginning of 2026, the size of the Ethereum validator staking entry queue has expanded significantly. The amount of ETH waiting to be staked has increased more than fivefold since the start of the year, currently reaching 2.582 million ETH—the highest level since early August 2023—with a corresponding wait time of over 44 days. Meanwhile, the validator exit queue has been completely cleared. After previously peaking at over 2.6 million ETH in September 2025, the number has now dropped to zero, indicating a clear structural reversal in capital flow on the staking side.
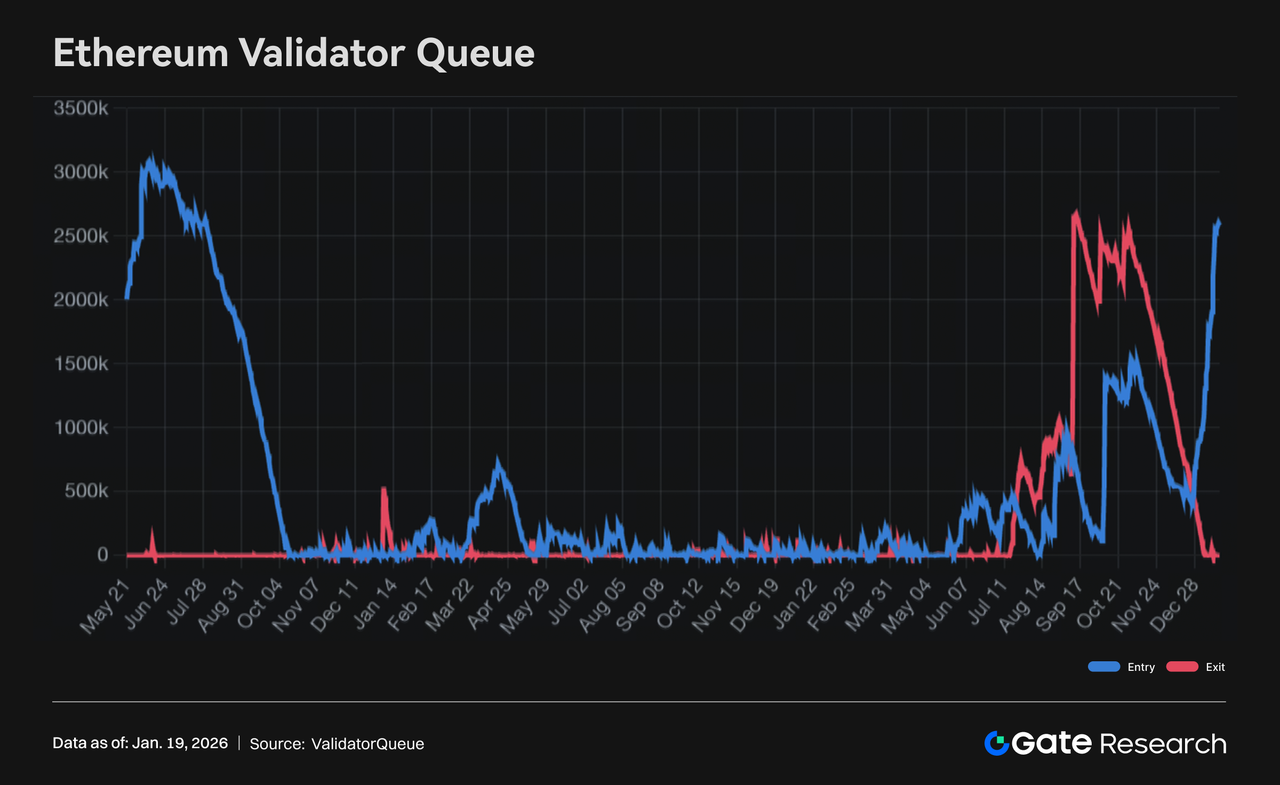
While price is under pressure, there is a clear increase in long-term staking commitment, showing a contrasting capital behavior compared to the recent ETH pullback and broader market deleveraging. The sharp rise in the staking entry queue, combined with the disappearance of the exit queue, indicates that there has been no significant outflow of long-term capital during the downturn. On the contrary, more ETH is actively being locked up, delaying its return to circulation.
Should Protocols Stop Evolving? A Divergence Between Ethereum and Solana
Recently, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik and Solana co-founder Toly engaged in a heated debate over whether protocols should cease evolving. Vitalik emphasized the “walkaway test” and “ossification,” essentially addressing a fundamental question: if all core developers were to walk away, could the chain still exist long-term as trustworthy infrastructure? In his view, a truly mature public blockchain should resemble foundational tools in the physical world—once the core rules are established, changes should be minimized. The goal is to maximize decentralization and censorship resistance through extreme protocol-layer stability. Ethereum, therefore, is increasingly focused on subtractive design—creating a “permanently usable minimal trust kernel”—pushing innovation toward clients, parameter layers, or applications rather than continuously altering the consensus or core protocol.
Solana, on the other hand, takes the opposite approach, treating “evolvability” itself as a core competitive advantage. Toly’s stance contrasts sharply: he does not see “whether developers can safely walk away” as a meaningful goal. Instead, the ability to evolve continuously is viewed as the protocol’s lifeblood. In Solana’s worldview, if the protocol stops iterating based on real user and developer needs, it effectively forfeits its place in the competition. Conversely, as long as the network continues to create real utility and enables developers to profit, it will naturally attract contributors to improve it—even potentially governed and optimized in the future by AI or LLMs. In this model, the protocol isn’t a “finalized tool,” but a system that must keep upgrading. The key question isn’t “should it change,” but “does it solve real problems,” and whether it has the capacity to say “no” to proposals that lack value.
Thus, this isn’t merely a debate between conservative and radical approaches, but a clear divergence in philosophy: Ethereum trades dynamism for long-term trustworthiness, while Solana embraces continuous evolution in pursuit of real-world competitiveness.
Invisible Security Risks Behind Auto-Execution in IDEs Amid the Vibe Coding Trend
As more developers embrace Vibe Coding using tools like VS Code and its derivatives such as Cursor and Antigravity, there’s a growing trend of frequently cloning projects and quickly running code. However, many overlook a key hidden risk: the auto-execution capability built into IDEs themselves.
SlowMist founder Cos points out that the core vulnerability lies in the “Allow Automatic Tasks” feature. When enabled, simply opening a project directory can silently trigger commands hidden in .vscode/tasks.json. In a carefully crafted attack, a seemingly ordinary GitHub clone can escalate into a full-blown supply chain intrusion.
A zero-cost yet highly effective risk mitigation step is to disable this feature. Press CTRL + SHIFT + P to access settings, then turn off Allow Automatic Tasks, or directly set “task.allowAutomaticTasks”: “off” in your user settings JSON. This blocks most stealthy “open-and-execute” attack paths. The change has minimal impact on typical development workflows, since most developers don’t require tasks to auto-run when opening a directory.
For Cursor users, enabling Workspace Trust adds another security layer. It prompts users to confirm whether they trust a workspace when opening a new directory. Even when marked as trusted, it prevents .vscode/tasks.json from being triggered automatically.
As AI-assisted programming pushes efficiency toward instant run-and-deploy, security boundaries must shift closer to the IDE layer. Otherwise, the most dangerous attacks won’t be about malicious code you ran—but about code you never clicked, yet was executed anyway.
References
- Gate, https://www.gate.com/trade/BTC_USDT
- Farside Investors, https://farside.co.uk/btc/
- Gate, https://www.gate.com/trade/ETH_USDT
- Farside Investors, https://farside.co.uk/eth/
- Gate, https://www.gate.com/crypto-market-data
- Investing, https://investing.com/indices/usa-indices
- Investing, https://investing.com/currencies/xau-usd
- CoinGecko, https://www.coingecko.com/en/cryptocurrency-heatmap
- ValidatorQueue, https://www.validatorqueue.com/
- X, https://x.com/toly/status/2012541454669783314?s=20
- X, https://x.com/evilcos/status/2012724893235003803?s=20
Gate Research is a comprehensive blockchain and cryptocurrency research platform that provides deep content for readers, including technical analysis, market insights, industry research, trend forecasting, and macroeconomic policy analysis.
Disclaimer
Investing in cryptocurrency markets involves high risk. Users are advised to conduct their own research and fully understand the nature of the assets and products before making any investment decisions. Gate is not responsible for any losses or damages arising from such decisions.
Related Articles

Exploring 8 Major DEX Aggregators: Engines Driving Efficiency and Liquidity in the Crypto Market

What Is Copy Trading And How To Use It?

What Is Technical Analysis?

How to Do Your Own Research (DYOR)?

12 Best Sites to Hunt Crypto Airdrops in 2025


