What is Aevo Coin?

What Is Aevo Token (AEVO)? Definition and Key Features
Aevo Token refers to AEVO, the native utility and governance token of the Aevo Exchange. AEVO powers governance voting, ecosystem incentives, and fee-related mechanisms. A decentralized exchange (DEX) operates through smart contracts rather than centralized custody, enabling trustless trading. Derivatives are contracts whose value is pegged to an underlying asset, such as BTC or ETH. An option gives the holder the right to buy or sell an asset at a set price before or at expiry. Perpetual contracts are leveraged instruments with no expiry date, maintaining price alignment via funding rates.
Aevo runs on Ethereum Layer 2 (L2) called “Aevo L2,” built with the OP Stack. This architecture aims to optimize both security and efficiency for high-performance derivatives trading.
Current AEVO Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply
As of January 19, 2026 (data provided by users), AEVO trades at approximately $0.037990. The circulating supply stands at 916,111,245.401012 tokens, with both total and maximum supply capped at 1,000,000,000 AEVO. Circulating market capitalization is about $37,990,000, with a fully diluted valuation (FDV) also at $37,990,000, accounting for roughly 0.0011% market share.
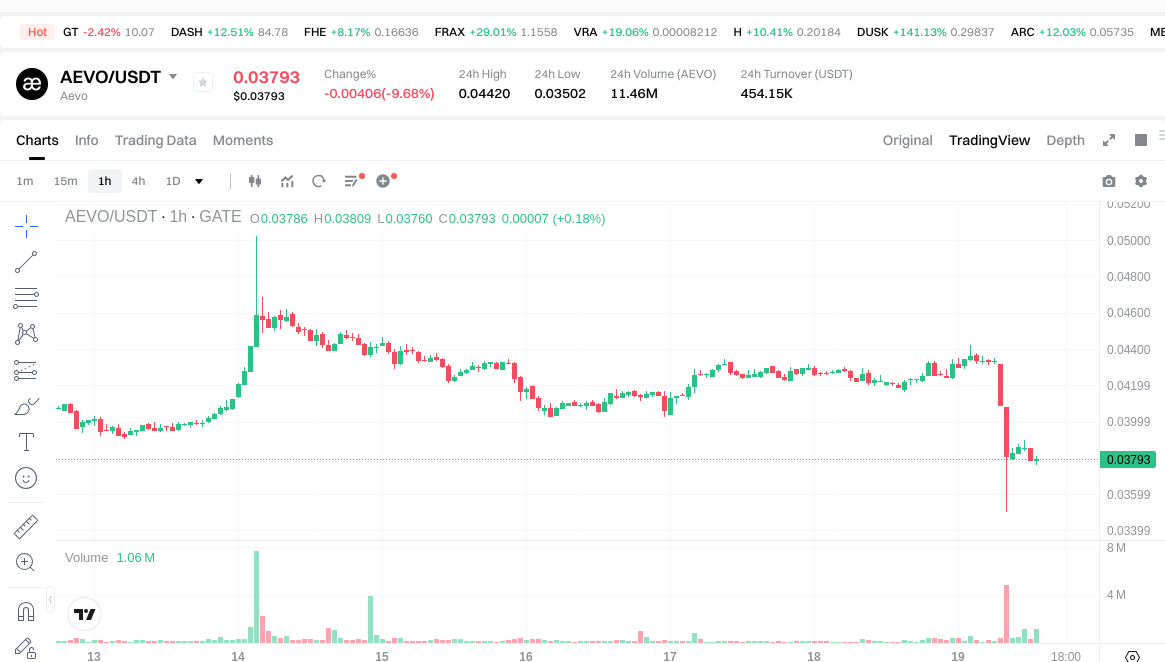
View AEVO/USDT Price
Short-term price changes: +0.16% over 1 hour, -9.72% over 24 hours, -8.86% over 7 days, +4.26% over 30 days. The 24-hour trading volume is approximately $444,073.
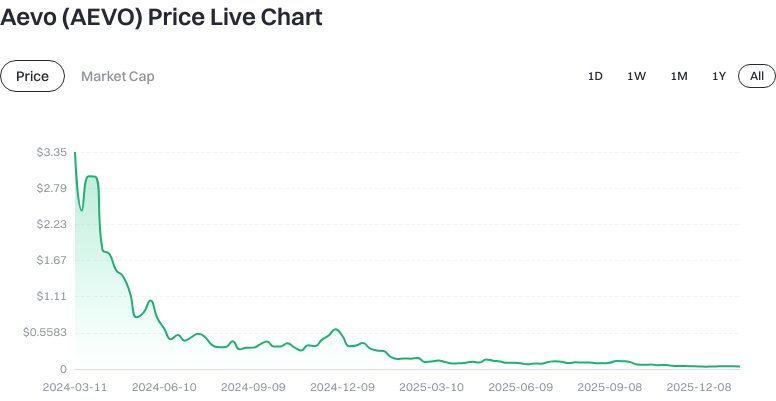
Circulating supply reflects the number of tokens available for trading on the market. Total supply is the cumulative amount issued, and maximum supply denotes the upper limit. Fully diluted valuation estimates total value at max supply. Prices fluctuate with market dynamics; always refer to Gate’s live data for actual trading.
Who Created Aevo (AEVO) and When?
AEVO was launched on March 12, 2023 (source: user-supplied information). The Aevo team developed the exchange within the Ethereum ecosystem and deployed it on the OP Stack-based Aevo L2 network. The goal is to maintain Ethereum-level security while delivering lower transaction costs and higher throughput for trading options and perpetual derivatives.
How Does Aevo Token (AEVO) Work?
Aevo operates on Aevo L2, an Ethereum Layer 2 solution. L2 networks process transactions off the mainnet and periodically submit data or proofs to Ethereum for settlement and security. The OP Stack is a modular framework for building Optimistic Rollup-based L2 networks. Transactions are executed optimistically; if disputes arise, challenges can be initiated on mainnet.
DEXs on Aevo use smart contracts for custody and settlement. Order matching may occur on-chain or via hybrid methods—off-chain matching with on-chain settlement—to balance speed and transparency.
AEVO serves as the protocol token and is typically used for governance voting (such as parameter adjustments), ecosystem rewards, and fee mechanisms. Actual implementation details should be referenced from official announcements.
Main Use Cases of Aevo Token (AEVO)
Common AEVO applications include:
- Participating in governance votes (e.g., adjusting fees or incentive programs)
- Receiving trading fee discounts or rebates during events
- Incentivizing liquidity providers and market-making activity
Some protocols offer staking or locking mechanisms for additional benefits; users should consult Aevo’s latest official statements for eligibility. For regular users, AEVO can also be held as a portfolio asset and used in ecosystem products or governance processes according to individual risk management strategies.
Wallets and Extension Solutions in the Aevo Ecosystem
Aevo L2 is compatible with Ethereum wallets—both browser-based and mobile options are supported. General setup steps:
- Add Aevo L2’s RPC endpoint and chain ID in your wallet.
- Bridge assets from Ethereum mainnet or other L2s to Aevo L2 using official bridges or cross-chain services.
- Trade or participate in governance on Aevo DEX or related contracts.
For security, hardware wallets are recommended for long-term self-custody. Always verify contract addresses and signature requests before interacting. Cross-chain operations or bridging incur fees and may require confirmation time; ensure you have sufficient ETH or L2-native gas assets to cover these costs.
Key Risks and Regulatory Considerations of AEVO
Derivatives are complex instruments—leverage and funding rates can amplify gains and losses, increasing overall risk if not managed properly.
Technical risks include smart contract vulnerabilities, cross-chain bridge exploits, and issues in the optimistic challenge mechanism of Layer 2 networks. Market risks encompass price volatility and liquidity shortages. Governance parameters may change; always monitor official updates.
On compliance: some jurisdictions strictly regulate derivatives trading and token usage—understand local laws before participating.
Account security and private key management are crucial: enable two-factor authentication and withdrawal whitelists for exchange accounts; securely back up mnemonic phrases for self-custody wallets; watch out for phishing attempts and malicious approvals.
How to Buy and Safely Store Aevo (AEVO) on Gate
Step 1: Register or log in to your Gate account, complete identity verification (KYC), activate two-factor authentication (2FA), and set up anti-phishing codes to enhance account security.
Step 2: Fund your account by depositing USDT or purchasing stablecoins via fiat channels on Gate to prepare for buying AEVO.
Step 3: In the spot trading section of Gate, search for “AEVO” and select your desired trading pair (e.g., AEVO/USDT). Place a market or limit order as needed; upon execution, check your holdings in the funds page.
Step 4: For self-custody, withdraw AEVO to your personal wallet. Add Aevo L2 network settings in your wallet; test with a small withdrawal to confirm accuracy before transferring larger amounts.
Step 5: Ensure secure storage—back up seed phrases offline; enable wallet permission controls and review authorizations regularly; use hardware wallets for large holdings; activate withdrawal whitelists and limits on Gate.
Step 6: Manage your assets proactively—track official updates regarding governance or incentive programs; assess returns and risks; avoid excessive leverage or frequent authorizations.
Comparison: Aevo Token (AEVO) vs dYdX (DYDX)
Both platforms target derivatives markets but differ in focus. Aevo supports both options and perpetual contracts, while dYdX is primarily known for perpetuals with limited options support. Technically, Aevo operates on an OP Stack-based Ethereum L2; dYdX v4 uses a standalone chain built on Cosmos (as of January 19, 2026, per public docs and community info).
Both tokens serve governance and incentive functions but have distinct mechanisms and distribution rules—refer to each project’s official documentation for details.
Aevo offers high compatibility with Ethereum wallet ecosystems; dYdX’s independent chain requires specific wallets and cross-chain procedures. Users should choose based on product needs (such as options availability), existing wallet setups, and network preferences.
Summary of Aevo Token (AEVO)
Aevo Token is the native utility token for Aevo—a derivatives DEX built on Ethereum Layer 2 (Aevo L2), serving both options and perpetual contract markets with integrated governance and incentive mechanisms. Market data indicate clear supply and market cap figures for AEVO, but prices remain subject to liquidity conditions and sentiment shifts.
The protocol leverages OP Stack-based Layer 2 technology for efficiency while inheriting Ethereum’s security guarantees. Practically, users can purchase AEVO on Gate, set up account security measures, self-custody assets as needed, and participate in ecosystem activities.
Given the complexity of derivatives—and technical risks inherent in Layer 2 and cross-chain operations—it is essential to stay updated via official announcements and security bulletins while exercising caution in fund management, approvals, and leverage use.
FAQ
What Advantages Does Aevo Have Over Other Derivatives Platforms?
As an Arbitrum-based on-chain derivatives trading platform, Aevo offers lower trading fees, faster execution speeds, and user-controlled asset custody. Unlike centralized exchanges, Aevo ensures that you retain ownership of your assets without needing to trust third-party custodians—making it ideal for traders who value self-sovereignty.
What Should Beginners Prepare Before Trading Derivatives on Aevo?
You’ll need a wallet compatible with the Arbitrum network (e.g., MetaMask) and sufficient funds for trading. It’s recommended to purchase USDC or ETH on Gate first, transfer to your wallet, then connect to the Aevo platform. Start small to familiarize yourself with platform operations before increasing trade size—derivatives involve significant risk.
What Are Common Risks When Trading Derivatives on Aevo?
The primary risk is leverage amplification—small price moves can lead to full liquidation. Watch out for slippage, funding rate costs, and smart contract vulnerabilities as well. Set stop-loss orders, avoid excessive leverage, and regularly check platform security audits to minimize risk.
What Are the Practical Uses of AEVO Tokens?
AEVO serves as the governance token for the Aevo platform—holders can vote on major decisions and feature roadmaps. AEVO can also be used to pay trading fees at a discount and may earn additional rewards in certain campaigns. Overall, AEVO aligns platform governance rights and economic incentives with its community.
How Does Aevo Ensure Fund Security?
As an on-chain platform, user funds are stored in smart contracts rather than centralized accounts—the main security factor is smart contract audit quality. While Aevo has undergone audits by reputable firms, blockchain protocols always carry code risk. Only commit what you can afford to lose, and monitor official security updates.
Quick Reference Glossary: Core Aevo (AEVO) Terms
- Options Trading: The right to buy or sell assets at a predetermined price by a specific date—Aevo focuses on derivatives trading.
- Derivatives: Financial instruments based on price movements of underlying assets; includes options, futures, etc.
- On-chain Trading: Transactions executed directly on blockchain without centralized intermediaries.
- Smart Contracts: Programmatic code that enforces trading rules automatically—ensuring options contracts settle as agreed.
- Liquidity Pools: Contracts that aggregate user funds to provide liquidity for trading pairs while generating fee income.
Further Reading & References
-
Official Site / Whitepaper:
-
Developer Resources:
-
Authoritative Media & Research:
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?
