What is Coti Coin?
What Is COTI?
COTI is a payment and settlement ecosystem centered around the concept of a “financial blockchain,” with its native token symbolized as COTI. Unlike traditional blockchains, COTI uses a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) to record transactions, aiming to deliver high throughput, low fees, and fast confirmation for use cases such as merchant acquiring, cross-border payments, and stablecoin settlements.
A DAG organizes transactions as nodes connected by directed edges, eliminating the need for block-based queuing and significantly increasing transaction throughput. Building on this structure, COTI provides financial infrastructure that supports multi-asset issuance and settlement. The COTI token is used to pay network fees, incentivize validator nodes, and participate in governance.
COTI (COTI) Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply
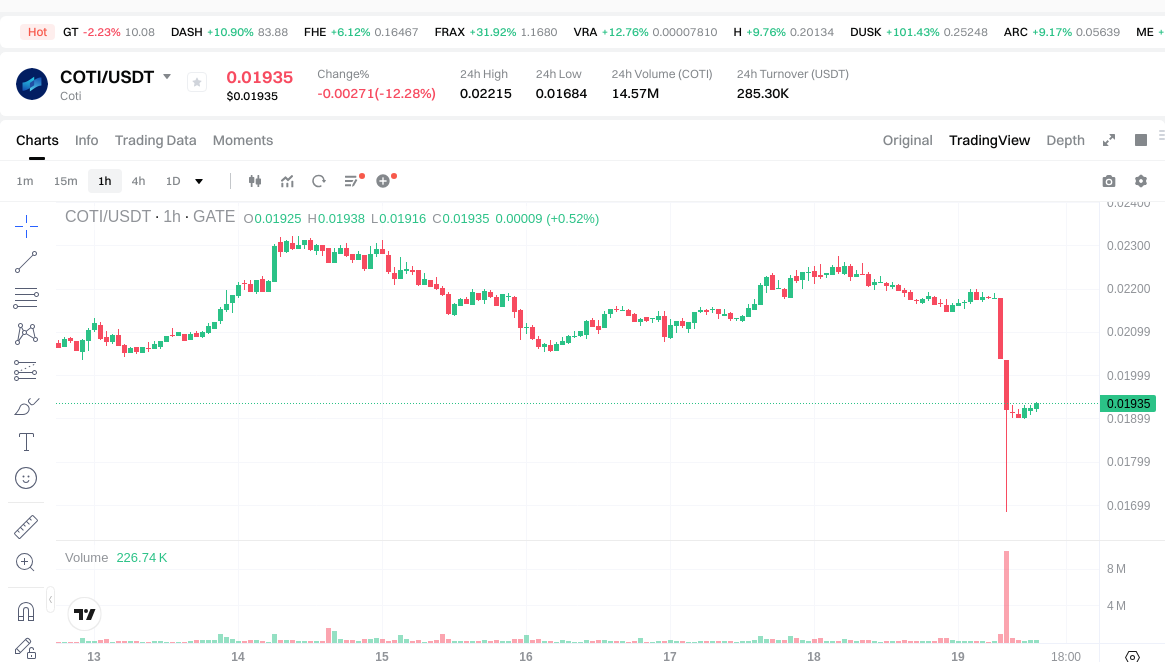
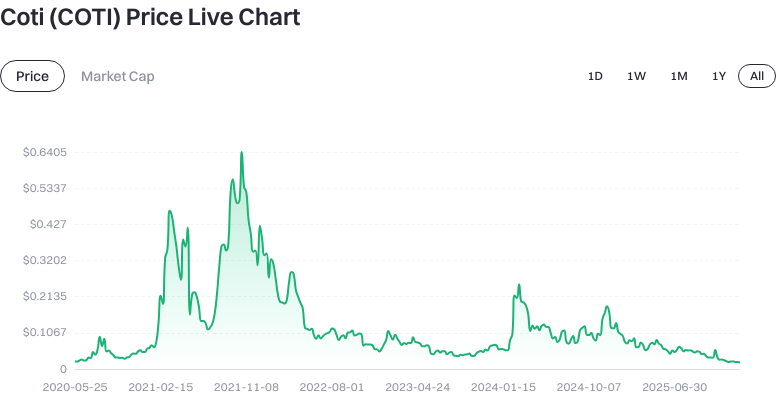
As of 2026-01-19 (source: input data), the price of COTI is approximately $0.019310, with a circulating supply of about 2,605,184,962 tokens. The total supply is approximately 2,605,199,700 tokens, and the maximum supply is set at 4,910,000,000 tokens.
Click to view COTI USDT Price
The circulating market capitalization is around $50,306,406, with a fully diluted valuation (FDV) of about $50,306,406 and a market dominance of approximately 0.0015%. The 24-hour trading volume is around $282,403. In terms of recent price movements, the 1-hour change is roughly +0.67%, 24-hour change -12.68%, 7-day change -9.86%, and 30-day change -10.48%.
Click to view Latest COTI Price Chart
Note: Fully Diluted Valuation (FDV) is typically calculated as “price × max supply.” The actual reported figures may vary due to token lock-up releases, circulating supply definitions, or network upgrades. Please refer to the provided data for accuracy.
Who Created COTI (COTI), and When?
The COTI project began development around 2017 and launched its mainnet and token on June 3, 2019 (source: input data). Officially positioned as a “blockchain alternative for finance,” COTI aims to deliver technology tailored to payment and merchant settlement needs for enterprise-grade applications.
Public records show that since launch, COTI has iterated on its multi-DAG architecture and merchant acquiring modules. It has also contributed to stablecoin infrastructure development—for example, collaborating on stablecoin solutions for the Cardano ecosystem that reached implementation in 2023 (as of October 2024; source: project announcements and community information).
How Does COTI (COTI) Work?
COTI organizes its transaction ledger as a DAG rather than a single-chain block structure. In simple terms: each transaction references previous ones to form a directed graph; nodes validate transactions in parallel, eliminating bottlenecks and boosting TPS (transactions per second).
- Consensus & Validation: COTI’s network employs a trust-based and topology-aware validation process to confirm transactions, reducing congestion and latency.
- Multi-DAG & Assets: The multi-DAG architecture enables issuance and settlement of various assets within one ecosystem—accommodating merchants, stablecoins, and cross-chain settlements.
- Fees & Token Utility: The COTI token serves as payment for network fees, incentivizes validator participation, and is used in governance or treasury management tools.
What Can You Do With COTI (COTI)?
- Merchant Acquiring & Settlement: E-commerce or brick-and-mortar merchants can accept payments via COTI’s modules, benefiting from low fees and rapid settlements.
- Cross-Border Payments: Businesses or individuals can use COTI’s high-speed DAG infrastructure for international transfers—reducing wait times and remittance costs.
- Stablecoin Issuance & Clearing: Supports issuing and settling stablecoins for hedging volatility and streamlining reconciliation processes.
- Accounts & Tools: Integrate with wallets and account management tools for fund management, fee estimation, and transaction history queries.
Actual performance depends on merchant adoption, regulatory landscape, and network activity. Key indicators include active addresses, transaction volume, and number of merchant integrations.
Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for COTI (COTI)
- Technical Risks: DAG architectures require robust network topology and validation mechanisms. Issues like consensus failures, network forks, or software bugs can compromise security or finality.
- Liquidity Risks: Low trading volumes can lead to significant slippage for large orders, impacting execution price and efficiency.
- Custodial Risks: Storing assets on exchanges or third-party custodians carries platform and account security risks; self-custody requires secure management of private keys and mnemonic phrases.
- Regulatory & Compliance Risks: Jurisdictions vary in their regulation of payments, stablecoins, and crypto assets—potentially affecting merchant onboarding or product structure.
- Network Version & Chain Selection: Differences in network versions or cross-chain representations may exist; always confirm the correct chain before deposits or withdrawals to avoid asset loss.
What Is the Long-Term Value Proposition of COTI (COTI)?
COTI’s long-term value depends on the extent of real-world adoption in payments and settlements. If merchants and institutions continue integrating COTI’s high-throughput DAG technology for low-cost processing, network effects may emerge—while stablecoin and multi-asset settlements can increase stickiness and revenue streams.
Key metrics to monitor include: active addresses and TPS; merchant and payment channel integrations; stablecoin circulation and clearing volumes; cross-chain compatibility; developer ecosystem activity; as well as ongoing improvements in fees and confirmation times.
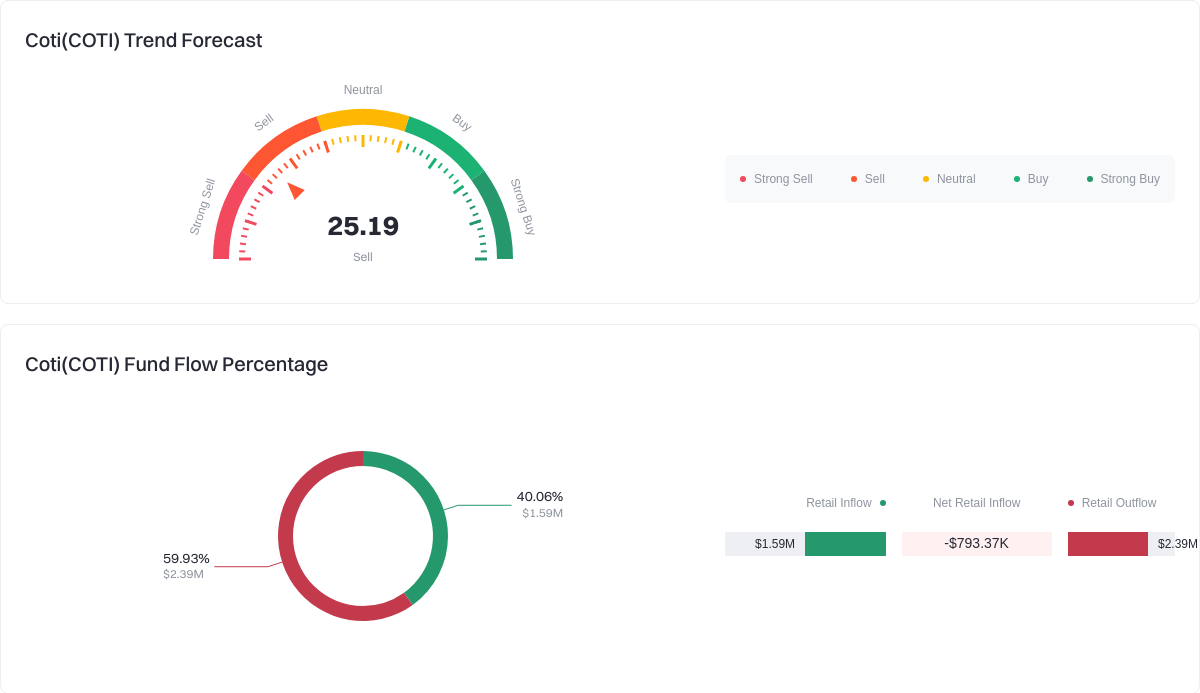
Click to view COTI Fund Flow Breakdown
Effective governance design and sound tokenomics also help drive sustainable value.
How to Buy and Safely Store Coti (COTI) on Gate
Step 1: Register and complete identity verification. Sign up at gate.com with a strong password, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), and complete KYC to increase deposit/withdrawal limits.
Step 2: Deposit funds. On the “Wallet” page, deposit USDT or supported fiat currencies. Transfer funds to your spot trading account to prepare for trading.
Step 3: Place an order to buy COTI. Search for trading pairs like “COTI/USDT” on the spot trading page. Use limit orders to set your own price/quantity or market orders for immediate execution at current prices. Check order book depth and potential slippage before trading.
Step 4: Withdraw or hold assets. For long-term self-custody, go to “Withdraw,” select the correct network/address—test with a small amount before larger withdrawals. If holding on-platform, enable withdrawal whitelist, anti-phishing code, and security alerts.
Step 5: Secure storage. For self-custody, use a compatible wallet—back up your mnemonic phrases and private keys securely offline. For large holdings, consider hardware cold wallets. Since COTI may exist on multiple networks, always confirm wallet compatibility and address format with your target chain.
How Does COTI (COTI) Compare to IOTA?
- Technical Implementation: Both utilize DAG technology. COTI focuses on financial-grade multi-DAG structures for merchant settlement; IOTA’s “Tangle” targets IoT use cases emphasizing micropayments and machine-to-machine communication.
- Application Focus: COTI specializes in merchant acquiring, stablecoin use cases, and cross-border settlement; IOTA is oriented toward IoT data integrity and the machine economy.
- Ecosystem & Tokenomics: COTI’s ecosystem expands around financial tools/payment channels; IOTA develops around device networks/data layers. Both require developer support but follow different growth paths.
Overall, COTI is geared towards payment networks for finance while IOTA emphasizes IoT and data networks—users should choose based on their specific needs.
Summary of COTI (COTI)
COTI positions itself as a DAG-based financial-grade payment and settlement network aiming to deliver high throughput with low fees for merchant acquiring, cross-border transfers, and stablecoin clearing. Current market data shows it sits within the mid-to-small cap segment with notable short-term volatility. Understanding its technical architecture, real-world application adoption, and compliance environment is crucial for assessing long-term value. When buying on Gate, follow steps for KYC completion, fund management, order placement, correct network withdrawals, and secure storage. It’s recommended to monitor ecosystem indicators such as merchant adoption rates, stablecoin usage scale, and on-chain activity to evaluate network utility and token value potential.
FAQ
Is Coti a good choice for beginners?
As a payment-layer solution, Coti is suitable for investors interested in blockchain-based payments. Beginners should familiarize themselves with its technical features and market risks before investing—starting with small amounts is advisable. Buying through reputable platforms like Gate can provide enhanced security. Always assess your risk tolerance before investing in any crypto asset—avoid following trends blindly.
What advantages does Coti offer compared to other payment cryptocurrencies?
Coti leverages DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) technology to deliver low transaction fees and high throughput—offering greater efficiency than traditional blockchains. Its focus on trust scoring and privacy protection within payments, combined with an innovative consensus mechanism that increases transaction speed, makes it particularly competitive for micropayments and cross-border transfers.
What earning opportunities are available for Coti holders?
Coti holders can earn rewards by participating in network validation (similar to staking), or through liquidity mining programs on platforms like Gate. Holding tokens also reflects confidence in the project’s long-term growth—but rewards are not guaranteed; it’s important to stay updated on project developments and market conditions.
How can I experience Coti’s payment features?
First purchase Coti through platforms like Gate. Then transfer it to a supported wallet app (such as the official Coti wallet). Merchants within the Coti ecosystem accept payments directly—you can use it for small transactions or remittances. Some wallets also support fiat conversion features. Start with small amounts to get comfortable with the process before scaling up usage.
How will technical upgrades impact Coti’s value?
Major updates such as DAG enhancements, ecosystem expansion, or regulatory developments can influence market expectations and price volatility. Monitoring official roadmaps and ecosystem progress is key to assessing long-term value—but remember that technical breakthroughs do not guarantee price increases; broader market sentiment and macro factors also play significant roles.
Glossary of Key Terms Related to Coti (COTI)
- Payment Channel: Core technology enabling fast, low-cost on-chain transaction settlement within the Coti network.
- DAG Structure: Directed Acyclic Graph technology adopted by Coti instead of traditional blockchain architecture to improve transaction throughput.
- Trust Scoring: Mechanism within the Coti network evaluating node reliability—influencing validation weight and rewards.
- Coti Wallet: Official wallet supporting payments and token management with integrated payment channel functionality.
- Node Staking: Users stake COTI tokens to become network nodes—participating in transaction validation and earning rewards.
- Transaction Fees: Fees paid for processing transactions on the Coti network—used to incentivize nodes maintaining network security.
References & Further Reading on Coti (COTI)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Media & Research:
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?
