What is Dogecoin?

What Is Dogecoin (DOGE)?
Dogecoin (DOGE) is a blockchain-based cryptocurrency that features a playful and approachable community culture. It is commonly used for peer-to-peer value transfers, including tipping creators, facilitating micro-payments, and supporting charitable fundraising.
As a cryptocurrency, Dogecoin relies on cryptography and a consensus mechanism to record transactions and prevent counterfeiting. The blockchain serves as a chronological ledger of all transactions, maintained collectively by network nodes—anyone can participate in or validate transactions.
Dogecoin (DOGE) Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply
As of 2026-01-14, DOGE is priced at $0.147750, with a circulating market cap of approximately $24,867,661,121.95 and a circulating supply of 168,303,363,126.579010 DOGE. The total supply stands at 168,309,043,126.579102 DOGE. The 24-hour trading volume is about $43,516,407.80.
In terms of short-term price action: the 1-hour change is -0.67%, 24-hour change is 6.44%, 7-day change is -0.37%, and the 30-day change is 8.10%. These figures indicate a mix of recent volatility and moderate growth over the past month.
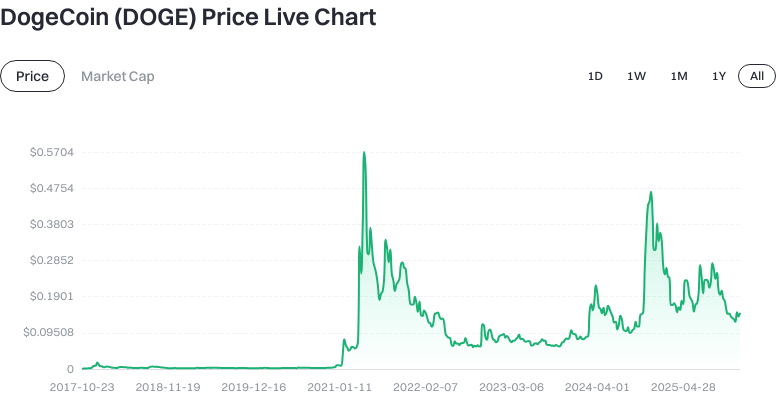
View the latest DOGE price trends
At this snapshot, fully diluted market capitalization aligns with circulating market cap at roughly $24,867,661,121.95. Since Dogecoin has no supply cap, "fully diluted market cap" is less meaningful; it’s more relevant to track current circulating market cap, issuance rate, and long-term inflation.
Data source: User-provided snapshot as of 2026-01-14.
Who Created Dogecoin (DOGE) and When?
Dogecoin was launched in December 2013 by Billy Markus and Jackson Palmer with strong support from the online community. Originating from the "doge" internet meme culture, Dogecoin was designed to lower participation barriers and foster friendly community interactions.
In its early days, Dogecoin was widely used for online tipping and charitable activities, helping DOGE gain popularity on social platforms and establish its distinct cultural identity. References: Public wikis and community documentation as of October 2024.
How Does Dogecoin (DOGE) Work?
Dogecoin operates on a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism where miners compete using computational power to bundle transactions into blocks and earn block rewards. This competitive system prevents double-spending and keeps the ledger consistent across the network.
Dogecoin utilizes the Scrypt algorithm—a hashing algorithm with a focus on memory intensity—differentiating it from Bitcoin’s SHA-256. DOGE’s block time averages around one minute, allowing for fast transaction confirmations. With its block reward fixed at 10,000 DOGE and no maximum supply limit, Dogecoin experiences ongoing inflation; however, as the overall supply grows, the inflation rate proportionally decreases.
To enhance network security and resource efficiency, Dogecoin supports merged mining with Litecoin—allowing miners to secure both blockchains simultaneously using the same computational power, which increases security and miner rewards. For more details, see the Dogecoin developer documentation and community resources as of October 2024.
What Can You Do with Dogecoin (DOGE)?
Tipping creators on social platforms is a signature use case for DOGE—users can easily send small amounts to show support thanks to low fees and fast confirmations.
Dogecoin is also popular for small cross-border transfers. Its peer-to-peer settlement model and rapid block times enable quick payments between friends or small merchants.
DOGE is frequently used in charitable fundraising and community-driven events, reflecting high engagement within its user base. Additionally, DOGE can be traded or included in investment portfolios on exchanges—users should always assess their risk tolerance before investing.
Wallets and Ecosystem Extensions for Dogecoin (DOGE)
Available wallet types include:
- Full Node Wallets: These synchronize the entire blockchain for maximum security but require significant storage and bandwidth; ideal for users with strict security or validation needs.
- Light Wallets & Mobile Wallets: These do not require downloading the full blockchain, making them user-friendly for daily payments and receipts.
- Hardware Wallets: Store private keys offline to reduce theft risk; best for long-term holding or large amounts.
- Multi-Signature Wallets: Require multiple private keys for authorization, enhancing security for organizations or teams.
Useful ecosystem extensions include browser extension wallets, block explorers (for viewing transactions and addresses), and payment plugins. When choosing a wallet, ensure it supports the native DOGE chain, check for open-source code and security audits, and back up your mnemonic phrase securely.
Key Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Dogecoin (DOGE)
Price Volatility: Crypto asset prices are influenced by market sentiment and liquidity; short-term fluctuations are common. Allocate DOGE according to your personal risk tolerance.
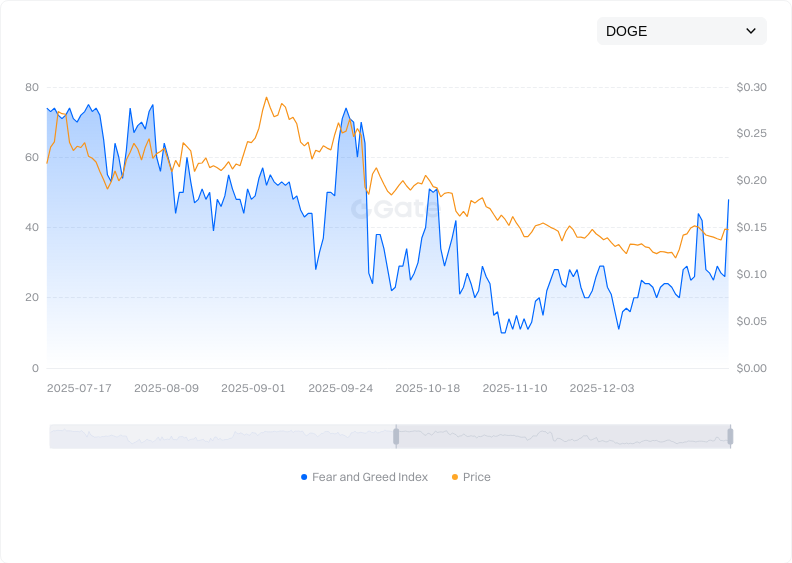
View the DOGE Fear & Greed Index
Inflation & Supply Risk: With no fixed supply cap, DOGE has ongoing issuance. Assess how new supply impacts returns relative to demand growth and network usage.
Network & Hash Rate Risk: Variations in hash power, miner concentration, and dependence on merged mining can affect network security and block stability.
Custody & Private Key Risk: Using exchanges or custodians exposes users to platform security threats. For self-custody, safeguard your private key or mnemonic phrase against phishing links and malware; enable two-factor authentication.
Regulatory Compliance: Jurisdictions differ in crypto trading rules, tax reporting requirements, and anti-money laundering standards. Understand your local regulations before fiat deposits or trading.
How to Buy and Securely Store Dogecoin (DOGE) on Gate
Step 1: Register a Gate account and complete identity verification. Enable two-factor authentication, set a strong password, and activate anti-phishing codes to secure your account.
Step 2: Deposit or purchase funds. You can buy USDT via fiat gateways or deposit crypto from other wallets into your Gate account—review Gate’s deposit instructions and risk disclosures.
Step 3: Select your trading pair. Search for DOGE in the spot market; common pairs include DOGE/USDT. Review pricing data, market depth, and recent volatility before trading.
Step 4: Place your buy order. Choose either limit or market order as needed; enter the amount and submit your order. After execution, verify your holdings on the asset page.
Step 5: Withdraw to a self-custody wallet if holding long-term. Copy your DOGE address (usually begins with “D”), select DOGE mainnet when withdrawing from Gate, and double-check your address and tag. Start with a small test withdrawal before transferring larger amounts; always consult Gate’s fee schedule and minimum withdrawal requirements.
Step 6: Secure storage & backup. Write down your mnemonic phrase offline and store it in multiple locations; consider using a hardware wallet. Regularly review your transaction history and device security status.
How Is Dogecoin (DOGE) Different from Bitcoin?
Supply Mechanism: Bitcoin has a hard cap of 21 million coins; DOGE has no supply limit and a fixed block reward—making it inherently inflationary over time. Bitcoin is seen as a scarce asset; DOGE is optimized for frequent micro-payments and tipping.
Algorithm & Block Time: Bitcoin uses SHA-256 with ~10-minute blocks; DOGE uses Scrypt with ~1-minute blocks for faster confirmations but different security/hash rate profiles.
Fees & Use Cases: DOGE typically has lower transaction fees suited for micro-transactions; Bitcoin’s higher fees and slower confirmations favor value storage or large transfers.
Culture & Community: DOGE is recognized for its lighthearted community culture and support of charitable initiatives; Bitcoin centers on decentralization narratives and long-term value storage—they occupy distinct roles in the crypto ecosystem.
Summary: Key Takeaways on Dogecoin (DOGE)
Dogecoin’s accessible community culture and fast confirmations have attracted a wide user base—most commonly for tipping and micro-payments. Its unlimited supply results in inflationary characteristics; long-term value depends on network usage and demand growth. Investors should monitor price trends, market cap, issuance rate, personal risk tolerance, and intended use of funds when allocating DOGE. Practically speaking, follow proper procedures on Gate for account creation and purchase; prioritize self-custody with careful private key backup and two-factor authentication. In dynamic markets, regularly reviewing positions and risks supports more stable investment strategies.
FAQ
Why Are Dogecoin Transactions Faster Than Bitcoin?
Dogecoin features a shorter block time (~1 minute) and higher block capacity compared to Bitcoin’s ~10-minute blocks—resulting in 10x faster transaction speeds for daily use cases. This enables rapid confirmations with low fees ideal for micro-payments but also means comparatively lower network security and decentralization.
Why Is Dogecoin Called a “Meme Coin”?
Dogecoin originated as an internet meme—its founders developed it as a humorous project without an initial supply cap (later revised to a 121 billion coin limit). Despite its playful origins, Dogecoin has earned recognition through strong community engagement and practical use cases. While lacking in technical innovation, its welcoming culture has become a unique advantage.
When Is the Best Time to Buy Dogecoin?
Dogecoin’s price is highly volatile—often influenced by public figures like Elon Musk or market sentiment. New investors may benefit from dollar-cost averaging to spread risk rather than attempting to time exact market bottoms. Set clear stop-loss/take-profit targets to manage emotional responses to volatility. Buying on reputable exchanges like Gate helps ensure fund safety.
Is Dogecoin’s Total Supply Really Unlimited?
Dogecoin was initially uncapped with about a 5% annual inflation rate. However, developers established a fixed supply cap of 121 billion coins in 2014—making it a capped cryptocurrency. While still much larger than Bitcoin’s 21 million supply (and thus more inflationary), DOGE no longer has unlimited issuance.
Why Is the Dogecoin Community So Active?
Dogecoin boasts one of the friendliest and most inclusive communities in crypto—a result of its playful nature and low entry barrier. Community members actively promote charity donations, tipping culture, and other applications—building strong social cohesion that drives value growth and attracts newcomers.
Glossary of Key Dogecoin (DOGE) Terms
- Proof of Work (PoW): A consensus mechanism where miners compete with computational power to package blocks and validate transactions; Dogecoin uses this system to maintain network security.
- Mining: The process by which miners solve mathematical problems with computing power to validate transactions and receive newly generated Dogecoins as rewards.
- Blockchain: A distributed ledger recording all Dogecoin transactions; composed of cryptographically linked blocks that ensure transaction immutability.
- Wallet: A tool for storing Dogecoin private keys and addresses; users manage their DOGE assets by sending, receiving, or controlling funds via wallets.
- Transaction Confirmation: The process where miners include Dogecoin transactions in blocks for network confirmation—the more confirmations, the more secure the transaction.
- Difficulty Adjustment: The process by which the Dogecoin network automatically adjusts mining difficulty based on hash power changes to maintain consistent average block times.
Dogecoin (DOGE): References & Further Reading
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Media / Research:
Related Articles

What Are Altcoins?

What is Blum? All You Need to Know About BLUM in 2025
