What is Gala Coin?

What Is Gala (GALA)? Definition and Core Meaning
Gala (GALA) is the utility token powering the Gala Games ecosystem, serving as a medium for in-game NFT purchases, event participation, fee payments, and as a form of reward for node operators. It supports a decentralized, multi-game content platform that connects players, developers, and node operators.
GALA has a capped total supply of 50 billion tokens, which helps ensure predictable long-term issuance. Users can earn GALA or limited-edition NFT rewards by operating Gala nodes or participating in ecosystem activities.
Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of Gala (GALA)
As of January 15, 2026, GALA is trading at approximately $0.007248 per token, with a circulating supply of about 47,064,391,639 tokens out of a maximum 50,000,000,000. The circulating market cap is around $341,122,710, with the same figure for fully diluted market cap and a market share of about 0.01%. The 24-hour trading volume is roughly $1,086,327. Recent price changes: +0.37% over 1 hour, -4.02% over 24 hours, +0.51% over 7 days, and +11.84% over 30 days.
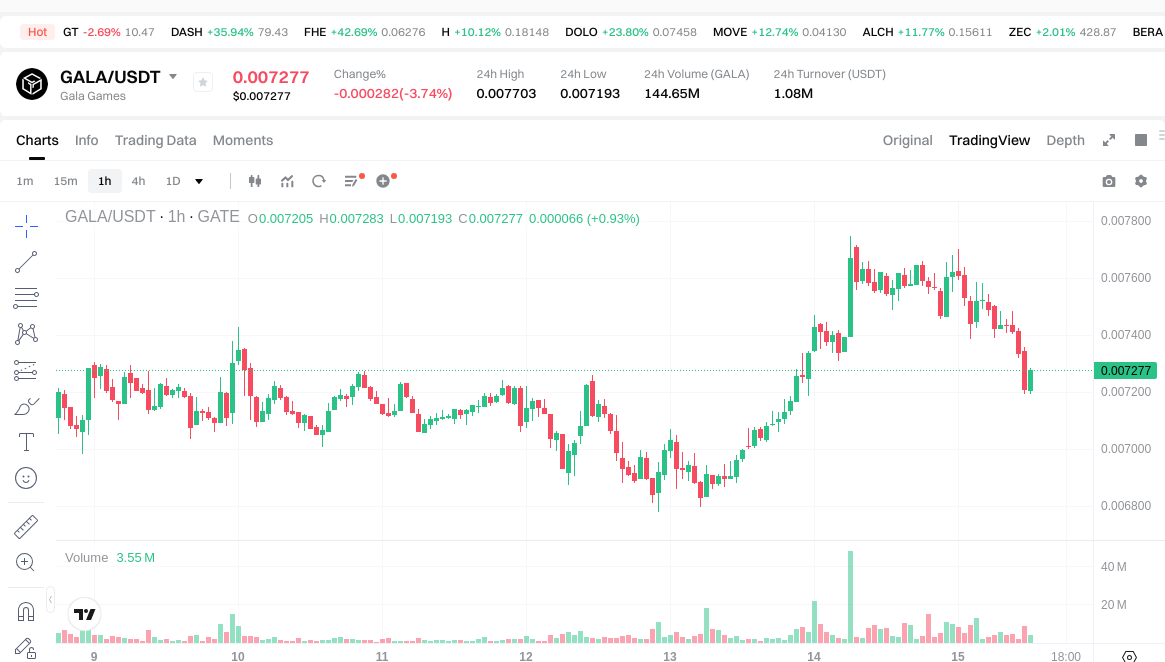
View the GALA/USDT price
"Circulating supply" refers to the number of tokens currently available for trading on the market. "Fully diluted market cap" estimates the market value if all possible tokens were in circulation. "Market share" indicates GALA’s proportion of the overall crypto market. Prices are subject to fluctuation—always verify the latest figures and market depth before investing.
Who Created Gala (GALA) and When?
Gala Games launched in 2020, founded by a team with backgrounds in gaming and blockchain. According to public information (as of October 2024), co-founders include Eric Schiermeyer (co-founder of Zynga) and game director Michael McCarthy, aiming to bring player rights and digital ownership into gaming economies.
GALA was first listed on September 17, 2020. Since launch, Gala has expanded its portfolio with several blockchain-based games and continued to develop its proprietary infrastructure.
How Does Gala (GALA) Work?
GALA acts as the native utility token within the Gala ecosystem, facilitating three main functions: purchasing NFTs and in-game items, incentivizing participants, and settling fees. Players use GALA for NFT/item purchases, developers and the platform use it for settlements or rewards, and node operators earn GALA and exclusive NFTs based on their contributions.
A "node" is a user-run network application that provides support such as network validation or content distribution; node operators earn rewards according to predefined rules. NFTs are unique digital assets recorded on-chain, commonly used for game items or collectibles.
According to public sources (as of October 2024), Gala is developing its proprietary chain—GalaChain—to lower transaction fees and improve performance. Initially, GALA circulated as an Ethereum ERC-20 token but is migrating toward its own chain and cross-chain solutions. "Gas fees" refer to the transaction costs required for on-chain operations; these fees vary based on network congestion.
What Can You Do with Gala (GALA)?
For players: GALA can be used to purchase in-game NFTs, join events or seasons, and pay minting or trading fees.
For developers: GALA serves as an economic module for settlement and incentive design—making it easy to issue game assets or structure rewards.
For node operators: Eligible operators can earn GALA and NFT rewards by following protocol rules.
For example: A player might use GALA to buy limited-edition skins within a Gala game or settle NFT trades on a marketplace. Node operators can claim periodic rewards by maintaining uptime and updating their software as required.
Key Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Gala (GALA)
Price Volatility: GALA’s price is affected by overall market trends and project developments, making it subject to short-term fluctuations.
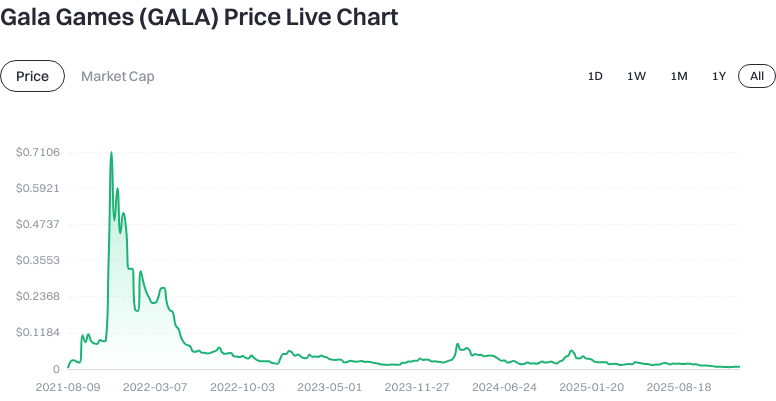
Technical & Migration Risks: The ecosystem is transitioning to GalaChain; bridging between networks, contract upgrades, and compatibility issues may introduce uncertainties.
Smart Contract & Asset Security: If smart contracts for games or NFTs have vulnerabilities or poor permission designs, asset security may be compromised. Always verify official contract addresses and signature details.
Node & License Rules: Node rewards depend on protocol changes, uptime requirements, and software versions; changes in license policy may impact expected returns.
Regulatory & Compliance Risks: Different regions have varying regulations for token trading and NFTs. Registration and trading on Gate may require KYC verification and compliance checks.
What Drives Long-Term Value for Gala (GALA)?
Long-term value depends on the ecosystem’s ability to deliver engaging content that retains users, the utility and diversity of NFT assets, the stability and sustainability of node incentives, as well as the performance and adoption rate of GalaChain by developers.
Key metrics to monitor include: active player base and retention rates; daily transaction volume for games and NFTs; on-chain transaction costs and confirmation times; number and activity of nodes; quality of developer partnerships and new content launches.
These factors collectively shape the demand for—and usage frequency of—GALA across the ecosystem.
How to Buy and Safely Store Gala (GALA) on Gate
Step 1: Register a Gate account and complete identity verification (KYC) using accurate information to meet platform and local regulatory requirements. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA).
Step 2: Prepare your funds by depositing stablecoins or fiat currency via supported channels—pay attention to deposit fees and processing times.
Step 3: Search for “GALA” on the spot market and select your preferred trading pair (e.g., GALA/USDT). Place a limit or market order according to your capital allocation and risk preference.
Step 4: After execution, check your balance in the asset page. Consider dollar-cost averaging (DCA) to reduce price volatility risk.
Step 5: Withdraw tokens to a personal wallet (optional). For long-term holding or frequent interactions, transfer GALA to a self-custodial wallet. Always double-check your recipient address and selected network (Ethereum or GalaChain); sending on the wrong network can result in loss of assets due to incompatible addresses or fees.
Step 6: Secure your holdings by backing up seed phrases and private keys offline with encryption. Activate 2FA and anti-phishing codes for both exchange accounts and wallets; keep software up-to-date.
Gala (GALA) vs Decentraland (MANA): Key Differences
Ecosystem Focus: GALA powers a multi-game platform; MANA is primarily used within Decentraland’s single virtual world economy for land, items, and events.
Token Utility: GALA emphasizes NFT purchases, rewards, and node incentives; MANA is mainly used for virtual land transactions, marketplace settlements, and event participation within Decentraland.
Technical Approach: Gala is developing its own GalaChain for improved performance; MANA remains an Ethereum ERC-20 token reliant on Ethereum scalability solutions.
Supply & Governance: GALA has a fixed maximum supply of 50 billion tokens; MANA’s supply and burn mechanisms are governed by its community and smart contracts. Their governance maturity and asset ecosystems differ significantly.
Summary of Gala (GALA)
Gala (GALA) is a utility token designed for multi-game ecosystems—connecting players, developers, and nodes—enabling NFT purchases, fee payments, and reward distribution. Its current market cap and supply suggest a mid-sized position within the crypto landscape; its price is influenced by both market trends and ecosystem growth. Long-term value depends on content quality, blockchain performance, developer adoption, ongoing migration to GalaChain, and evolving node policies. For practical use: follow step-by-step procedures on Gate for KYC verification, order placement, secure withdrawals, careful network selection, and private key management. Regularly track ecosystem metrics and risk factors before making allocation or holding period decisions.
FAQ
What Are the Main Use Cases for GALA?
GALA is the native token of the Gala Games platform—primarily used for in-game asset purchases, NFT transactions, and platform governance. Players can earn GALA through various blockchain games within the ecosystem and spend it on equipment, land parcels, or participate in community governance votes.
What Are the Benefits of Holding GALA?
Holding GALA provides access to gaming activities within the Gala Games ecosystem, enables NFT trading, grants voting rights in governance processes, and allows holders to benefit from ecosystem growth. On exchanges like Gate, GALA offers liquidity—enabling trading or cashing out as needed.
How Is GALA Different from Other Gaming Tokens?
GALA stands out because it is blockchain-based—giving players true ownership of digital assets (NFTs), as opposed to traditional game currencies which are limited to in-game balances. Additionally, GALA is tradable across platforms like Gate, while standard game currencies are usually locked within individual games.
How Can Beginners Get Started with GALA?
New users should register with a reputable exchange like Gate, purchase GALA using fiat or other cryptocurrencies, download Gala Games apps to try out games in the ecosystem, then store their GALA in a wallet or continue holding it on Gate. It’s recommended to start with small amounts while learning about platform operations and market conditions.
What About GALA’s Supply & Circulation?
GALA has a fixed maximum supply structure—supporting scarcity. A portion circulates freely in the market while another portion is released gradually as ecosystem incentives. For detailed supply data, refer to Gate’s market overview pages; understanding these metrics helps assess GALA’s investment potential.
Glossary: Key Terms Related to Gala (GALA)
- GameFi: The fusion of gaming with decentralized finance—players earn tokens and asset yields through gameplay.
- NFT (Non-Fungible Token): A unique digital asset representing ownership—commonly used for virtual items in games.
- Staking: Locking tokens within a network to earn rewards while supporting governance or security.
- Node: A computer running the Gala network—maintaining blockchain data and validating transactions.
- Smart Contract: Self-executing code that drives in-game economies and asset interactions.
- Cross-Chain Bridge: Technology connecting different blockchains—enabling asset movement and interoperability across networks.
Further Reading & References
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Media / Research:
Related Articles

The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges: Full-Chain Interoperability Becomes Inevitable, Liquidity Bridges Will Decline

Solana Need L2s And Appchains?
