What is LRC Coin?

What Is Loopring Protocol?
Loopring Protocol is a decentralized trading protocol built on Ethereum, characterized by off-chain order matching and on-chain settlement. This hybrid approach boosts transaction efficiency and reduces costs. Decentralization here means that no single intermediary is relied upon; instead, smart contracts (self-executing programs on the blockchain) handle settlements according to transparent rules. LRC is the native utility token of the Loopring ecosystem, used for trading fee discounts, incentives, and governance.
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of Loopring (LRC)?
As of January 20, 2026 (based on available market data), LRC trades at approximately $0.049180. The circulating supply is 1,245,991,468.94 LRC; the total supply is 1,373,873,397.44 LRC, and the max supply is capped at 1,374,513,896 LRC. The circulating market capitalization stands at around $67,567,093.69, with a fully diluted valuation of approximately $67,567,093.69.
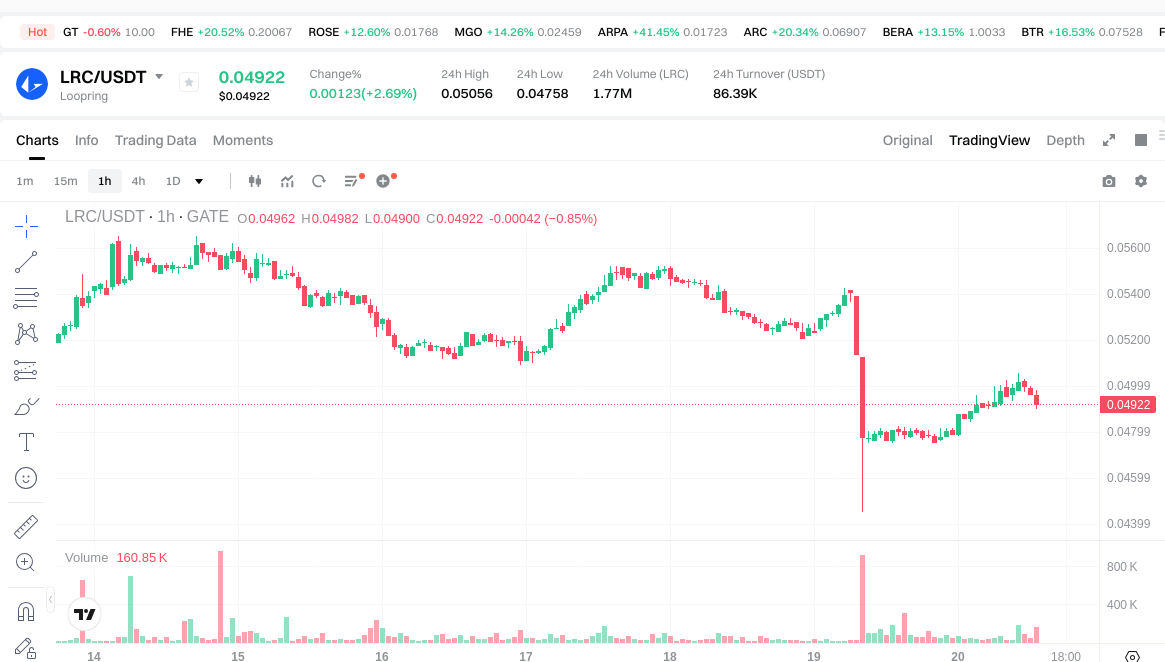
Click to view LRC USDT Price
Short-term price changes: -1.38% over 1 hour, +2.77% over 24 hours, -5.14% over 7 days, -15.87% over 30 days; 24-hour trading volume is about $86,665.90.
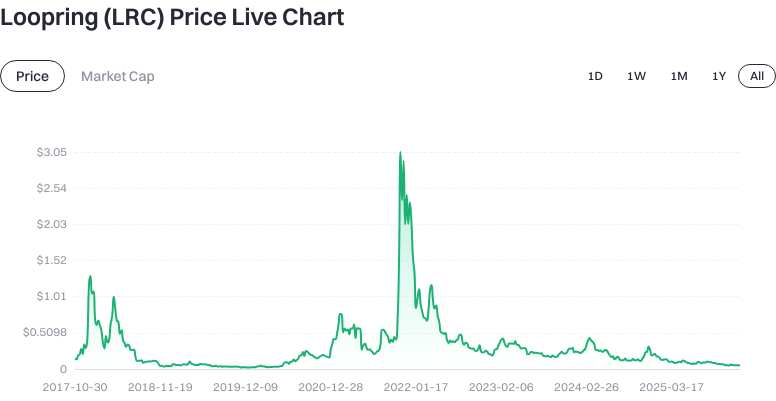
Click to view Latest LRC Price Data
Market cap dominance is around 0.002%. These metrics fluctuate with market dynamics and liquidity—always verify up-to-date figures before investing.
Who Created Loopring (LRC), and When?
Loopring Protocol was launched by its team in 2017, with public sources commonly citing Daniel Wang as one of its early principal founders. The project issued LRC on Ethereum and has developed around decentralized exchange functionality. Later versions introduced zkRollup—a zero-knowledge proof-based scaling solution—to enhance order matching and settlement efficiency. The protocol and its front-end applications have continued to iterate in subsequent years.
How Does Loopring (LRC) Work?
Loopring employs an "off-chain order matching, on-chain settlement" model. Order matching pairs buy and sell orders; settlement refers to recording the final asset transfer on the blockchain ledger. The protocol leverages zkRollup, a layer 2 scaling solution that bundles multiple transactions and uses zero-knowledge proofs for mainnet validation—enabling high throughput and low fees.
Within this architecture, the matching engine processes the order book off-chain and generates matched results; asset settlements are then securely executed on-chain via smart contracts. This preserves the price discovery benefits of an order book while entrusting final settlement to Ethereum, minimizing custody risk.
LRC's role in the mechanism includes providing trading fee discounts and ecosystem incentives. Historically, the protocol has also explored staking and fee redistribution to encourage participation—specific arrangements depend on community consensus and version updates.
What Can You Do With Loopring (LRC)?
LRC holders can benefit in three main ways. First, enjoy reduced fees and transaction cost savings through discounts or offsets. Second, earn ecosystem incentives by providing liquidity or participating in protocol activities. Third, engage in governance by voting on parameters and upgrades (subject to current governance rules).
For typical users, the most direct use case is accessing Loopring-powered trading applications to enjoy lower costs and faster settlement—while retaining the ability to self-custody assets in a personal wallet.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Loopring (LRC)?
- Price Volatility: Crypto assets are subject to significant fluctuations due to liquidity and market sentiment.
- Smart Contract Risk: Even audited code may contain vulnerabilities or be exploited.
- Liquidity Risk: Low trading volumes may cause substantial slippage for order execution or large trades.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks for tokens and decentralized exchanges evolve across jurisdictions.
- Custody & Key Management Risk: Storing assets on exchanges or platforms carries counterparty risk; self-custody requires secure management of private keys (the secret strings that prove asset ownership), which cannot be recovered if lost.
What Is the Long-Term Value Proposition for Loopring (LRC)?
Long-term value depends on three factors. First, real usage and trading volume—can zkRollup’s low fees and high efficiency attract sustained users? Second, value capture—how well does the protocol return economic value generated from usage to LRC holders through fee discounts, incentives, or governance rights? Third, competitive positioning—can the order book model differentiate itself from AMMs and other models through superior price discovery or a professional trading experience?
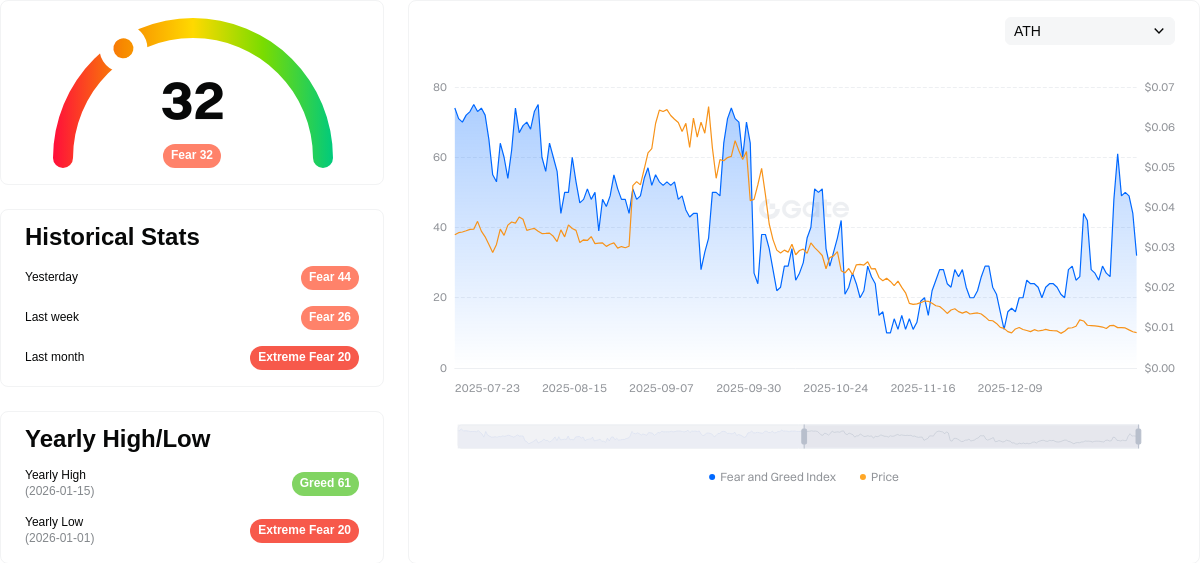
Click to view Crypto Market Fear & Greed Index
On the supply side, LRC’s max supply is around 1.374 billion tokens—providing a boundary for long-term evaluation, but actual value depends chiefly on demand and real-world use cases.
How Can I Buy and Safely Store Loopring (LRC) on Gate?
Step 1: Register and Complete KYC
Create an account on Gate’s website or app and complete identity verification to increase withdrawal and trading limits.
Step 2: Deposit Funds
Buy crypto with fiat or deposit stablecoins like USDT; then exchange for LRC on the spot market. Pay attention to the deposit network and confirmation times.
Step 3: Place a Trade
Search for "LRC" on the trading page and select spot trading. Use market orders for instant execution or limit orders to set your preferred price.
Step 4: Withdraw to a Self-Custody Wallet (Optional)
To manage your own assets, withdraw LRC to your personal wallet. Always store your seed phrase and private key securely—never enter them in untrusted environments.
Step 5: Security & Fee Management
Enable two-factor authentication and withdrawal whitelists; check withdrawal networks and fees; split large trades into smaller batches to minimize market impact.
How Is Loopring (LRC) Different From Uniswap (UNI)?
- Positioning & Mechanism: Loopring centers on order book matching accelerated by zkRollup; Uniswap is an automated market maker (AMM) relying on liquidity pools and constant product formulas for pricing.
- User Experience: Order books offer depth and limit order experiences similar to traditional trading, while AMMs can more easily bootstrap liquidity for long-tail assets but may introduce slippage or impermanent loss.
- Token Utility: LRC provides fee discounts, ecosystem incentives, and governance; UNI primarily functions as a governance token with voting rights over protocol parameters and treasury management.
- Value Capture: Both relate token value to protocol usage but differ in their fee distribution and tokenomics—users should monitor each protocol's latest governance decisions and economic models.
Summary of Loopring (LRC)
Loopring leverages zkRollup technology to enhance order book-based trading efficiency—off-chain matching with on-chain settlement strikes a balance between performance and security. LRC serves as the ecosystem token supporting fee discounts, incentives, and governance roles. Short-term price is highly sensitive to market fluctuations; long-term prospects rest on real user volume, value distribution mechanisms, and competitive differentiation. In practice, monitor protocol usage data and governance proposals closely; buy via Gate as needed and choose between exchange custody or self-custody based on your risk appetite—always prioritize account security and private key management.
FAQ
What Is LRC?
LRC is the governance token of Loopring Protocol—a decentralized exchange protocol built on Ethereum. Holders can participate in protocol governance decisions and receive a share of trading fees. LRC is traded on Gate and other major exchanges; its total supply is 137.5 million tokens.
What Are the Uses of LRC?
LRC has three main utilities:
- Governance voting—holders can vote on major protocol upgrades and decisions.
- Fee sharing—governance participants receive a portion of trading fees generated by the protocol.
- Community incentives—developers and liquidity providers are rewarded with LRC for their contributions.
How Does LRC Differ From Other Exchange Tokens?
LRC is specific to Loopring as a governance token—unlike exchange platform tokens such as BNB or FTT. Loopring focuses on on-chain order book models alongside automated market maker functionality, while different exchanges have distinct utility models for their tokens. When choosing an asset, consider the issuer, ecosystem scale, and your trading preferences.
Should I Hold LRC Long-Term?
Long-term holding depends on your investment strategy. If you believe in Loopring’s development prospects and want to engage in governance or revenue sharing, holding may make sense; if you are focused on short-term trades, you can respond flexibly to price movements. New users should study the protocol fundamentals and risks before deciding—avoid blindly following trends.
How Do I Buy LRC on Gate?
On Gate, simply search for an LRC trading pair to begin trading. Deposit fiat or other cryptocurrencies into your account first; then select an appropriate LRC pair (such as LRC/USDT), set your desired amount and price, and place your order. Beginners are advised to start with small amounts to get familiar with the trading interface and risk management.
Glossary of Key Loopring (LRC) Terms
- Layer 2 (L2): Ethereum scaling solutions that reduce costs and increase speed by batching transactions.
- Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZK-Proof): A cryptographic method for proving data validity without revealing its contents—a core technology for Loopring.
- Decentralized Exchange (DEX): An exchange enabling direct peer-to-peer trading; Loopring supports DEX transactions.
- Gas Fees: The cost required to execute transactions on Ethereum; L2 solutions significantly reduce gas costs.
- Liquidity Pool: A pool of user-deposited funds providing liquidity for trades in exchange for a share of fees.
- Smart Contract: Programmatic code that self-executes when preset conditions are met—drives all Loopring transactions and settlement processes.
Further Reading & Official Resources
-
Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Media / Research:
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?
