What is Solana?
What Is Solana?
Solana is a high-performance layer-1 blockchain protocol designed to support large-scale decentralized applications (dApps). It is a public chain that utilizes a delegated proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, allowing users to stake SOL tokens with validators to secure the network. Solana also integrates Proof of History (PoH) to synchronize time ordering, which enhances throughput, speeds up confirmation times, and reduces transaction fees.
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of Solana (SOL)?
As of January 19, 2026 (reference data), the price of SOL is approximately $133.72. The circulating supply is around 565,585,077.39 SOL, with a total supply of about 618,636,586.56 SOL. There is no fixed maximum supply. The circulating market capitalization stands at roughly $82,724,084,354.50, and the fully diluted market cap is estimated at the same value, representing about 2.52% of the market share. Recent price changes: 1-hour -0.069%, 24-hour -6.31%, 7-day -6.23%, 30-day +5.88%. The 24-hour trading volume is approximately $113,953,310.56.
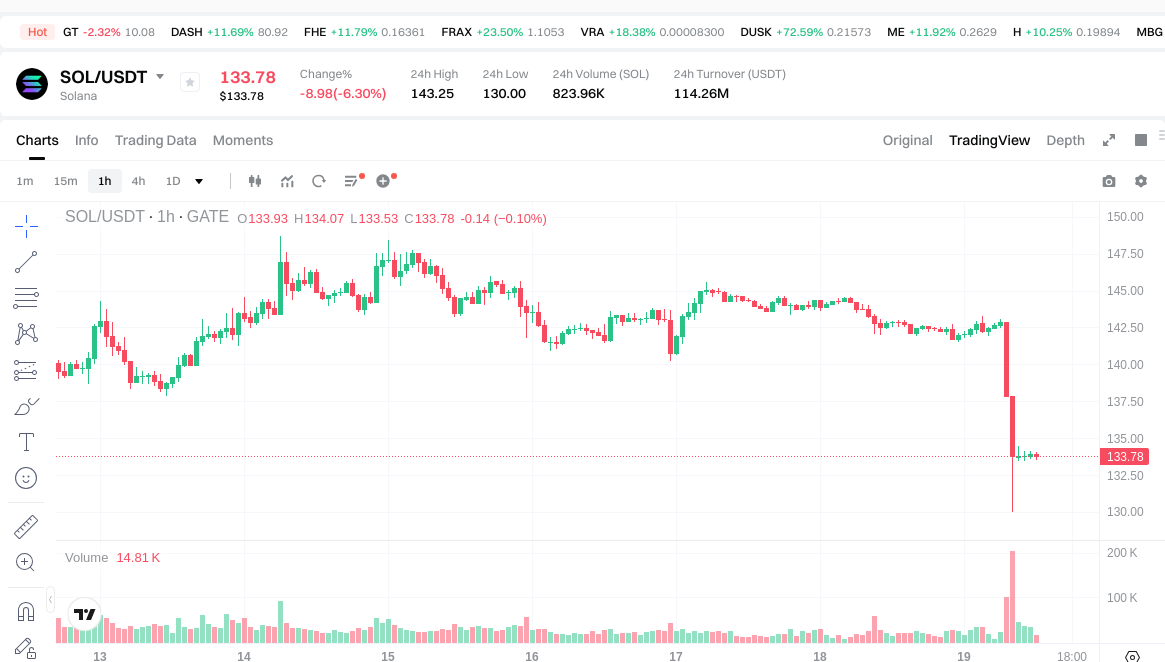
Click to view SOL USDT Price
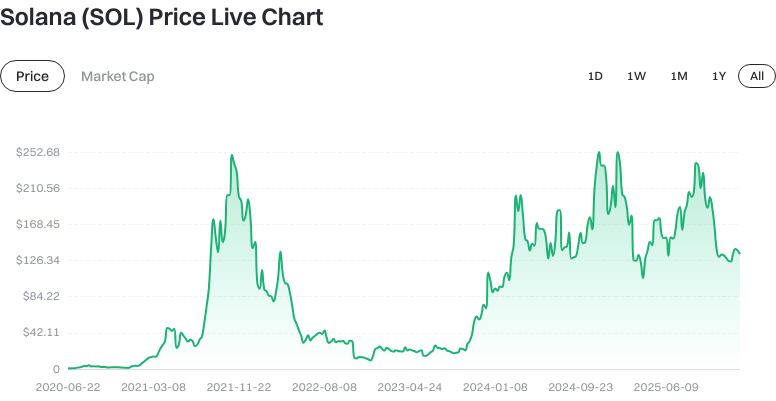
Click to view Latest SOL Price Trends
Market cap is calculated as price times circulating supply and reflects the current market scale; fully diluted market cap assumes all tokens are in circulation. The above price changes indicate short-term volatility—investment decisions should consider timing and risk tolerance.
Who Created Solana (SOL) and When?
Solana was initiated in late 2017 by a team of former engineers from Qualcomm, Intel, and Dropbox. One of the core creators is Anatoly Yakovenko. The mainnet launched on March 22, 2020, with the goal of providing high throughput and low-latency blockchain infrastructure without compromising decentralization or security.
How Does Solana (SOL) Work?
Solana operates on a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus where holders stake SOL to support validator nodes in block production and consensus, earning on-chain rewards. Staking involves locking tokens in the network to enhance security and earn yield.
Proof of History (PoH) is Solana’s cryptographic timekeeping method that timestamps transactions and messages, enabling verifiable ordering and reducing network coordination overhead—this boosts parallel processing and overall throughput.
On the execution layer, Solana processes transactions with a parallel execution framework to maximize transactions per second (TPS) and minimize confirmation time. It employs Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus for rapid finality, meaning transactions become irreversible within seconds.
What Can Solana (SOL) Be Used For?
Users can transfer value and make payments with SOL—its fast confirmations and low fees are ideal for micro-payments and high-frequency scenarios. Developers can issue tokens based on the SPL standard and build DeFi applications like decentralized exchanges, lending platforms, and yield aggregators.
In the NFT space, Solana enables minting and trading of digital collectibles. Games and social apps use the blockchain for item ownership or identity credentials, leveraging high concurrency for enhanced user experience. Enterprises and developers also explore settlement solutions, data integrity assurance, and on-chain proofs.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Solana (SOL)?
Price Volatility: Crypto assets are highly sensitive to market sentiment and liquidity; short-term swings do not guarantee long-term trends.
Technical & Network Risks: Past incidents include network outages or congestion, which in extreme cases may impact transaction confirmation and dApp availability.
Decentralization & Access: Validator nodes require substantial hardware and bandwidth resources, raising debates about true decentralization.
Smart Contract Risks: Vulnerabilities or governance errors in smart contracts can lead to fund losses; attention to audits and risk controls is crucial.
Regulatory & Compliance: Laws and tax requirements vary by region; participants must understand and comply with local regulations, including KYC/AML rules.
Account & Key Security: Exchange accounts should enable 2FA and phishing protection; for self-custody wallets, losing or exposing mnemonic phrases or private keys results in irrecoverable asset loss.
What Is the Long-Term Value Proposition of Solana (SOL)?
Solana’s long-term value hinges on its ability to sustain high throughput and low fees alongside continued growth of its developer and user ecosystem. Expansion into DeFi, NFTs, gaming, and payments could boost network activity and fee burning. SOL serves as both a staking asset for security and as transaction fee currency; the absence of a fixed supply cap means inflation and rewards must be monitored closely. Ongoing performance upgrades, stability improvements, and regulatory compliance will shape its competitiveness and adoption.
How Can I Buy and Safely Store Solana (SOL) on Gate?
Step 1: Register an account on Gate (gate.com) and complete identity verification (KYC) to ensure compliance and withdrawal permissions.
Step 2: Enable security settings—bind 2FA (such as dynamic code), set a fund password, activate withdrawal whitelist, and anti-phishing codes.
Step 3: Prepare funds by purchasing USDT via fiat channels or depositing crypto into your account; confirm receipt before trading.
Step 4: Search for “SOL” in the spot trading section, select an appropriate trading pair (e.g., SOL/USDT), review order book depth and recent trades.
Step 5: Place your order. Market orders execute instantly at current prices—ideal for quick buys; limit orders let you set your own price for controlled execution.
Step 6: Check your assets after purchase in the “Assets” page—confirm SOL balance and trade history; set price alerts or risk controls as needed.
Step 7: Withdraw to your self-custody wallet (optional). Copy your Solana wallet address, choose Solana as the withdrawal network, test with a small amount first before transferring larger amounts once confirmed.
Step 8: Secure storage—offline backup your mnemonic phrase and private key; keep them safe (do not photograph or store online). For long-term holding, use hardware wallets; periodically update wallet firmware and review security policies.
How Is Solana (SOL) Different from Ethereum (ETH)?
Consensus & Execution: Solana combines PoS with PoH for parallel transaction execution—delivering higher throughput with lower latency. Ethereum uses PoS with widespread rollup-based scaling; its mainnet emphasizes robustness and general-purpose compatibility.

Click to view Latest SOL Price Trends
Performance & Fees: Solana targets high TPS with minimal fees for frequent-use applications; Ethereum’s mainnet fees are higher but mitigated by layer-2 networks—supporting broader ecosystems and standardized toolchains.
Development & Ecosystem: Solana programs are typically built in Rust/C/C++, whereas Ethereum relies on EVM and Solidity—resulting in distinct developer experiences. Ethereum’s ecosystem is larger and more mature; Solana excels in high-performance applications and user experience.
Decentralization & Stability: Ethereum has a longer track record in decentralization and censorship resistance; Solana prioritizes performance but must continually strengthen network stability and validator diversity. Both chains suit different application scenarios based on their design philosophies.
Summary of Solana (SOL)
Solana is a public blockchain focused on high throughput and low transaction fees, leveraging PoS and PoH for rapid parallel execution—making it well-suited for DeFi, NFTs, and high-frequency applications. The above market data is as of January 19, 2026, reflecting current conditions only. To participate in Solana, users should understand its technical mechanisms, supply schedule, monitor network stability and ecosystem growth, and prioritize account/key security. Stepwise buying on Gate, prudent portfolio management, and careful risk assessment help newcomers enter confidently while tracking long-term value trends.
FAQ
How much faster are transactions on Solana compared to Ethereum?
Solana’s transaction speed far exceeds Ethereum’s—handling tens of thousands of transactions per second versus Ethereum’s approximate 15 TPS. This drastically reduces network congestion and gas fees on Solana.

Click to view SOL USDT Price
Solana’s high performance is powered by its unique Proof of History consensus mechanism—delivering smoother experiences for developers and users alike.
After buying SOL on Gate, how do I safely transfer it to my own wallet?
After purchasing SOL, you can withdraw directly to your personal Solana wallet address. Always start with a small test transfer from Gate to confirm the address is correct before moving larger amounts. Ensure you select the Solana mainnet (SOL Network) during withdrawal to prevent asset loss from incorrect chain selection.
Why does the Solana network sometimes experience outages?
Due to its high-performance architecture, Solana has faced outages during periods of surging network traffic. In extreme cases, validator nodes struggle to process rapid transaction spikes. The Solana team continues to optimize clients and upgrade infrastructure to improve stability—network reliability is steadily increasing.
What popular applications exist in the Solana ecosystem?
The Solana ecosystem features many leading dApps including DEXs (Raydium, Orca), NFT marketplaces (Magic Eden), lending protocols (Marinade), among others. These projects leverage Solana’s fast speed and low fees to deliver seamless trading experiences—making them excellent entry points for exploring real-world Solana use cases.
Besides trading/investing, what else can you do with SOL tokens?
Beyond trading, SOL serves as both a governance token and payment instrument on the Solana network. Holders can vote on protocol proposals, stake SOL for rewards, or use it within ecosystem dApps—for paying transaction fees or participating in liquidity mining activities. These functionalities give SOL practical utility across the network.
Glossary of Key Solana (SOL) Terms
- Proof of History: Solana’s unique consensus innovation—a cryptographic clock that timestamps events to prove their order, boosting transaction processing speed.
- Sealevel: The parallel runtime environment powering smart contract execution on Solana—enabling massive network throughput via concurrent operations.
- Program: Smart contracts within the Solana ecosystem—written primarily in Rust—capable of executing complex logic on-chain.
- Lamport: The smallest denomination of SOL; 1 SOL = 1 billion Lamports—used for precise valuation and transaction fee calculations.
- Rent: Data storage fee on Solana—calculated by storage size and duration; reclaimable by closing accounts.
- Validator: Network participants running Solana nodes—staking SOL to participate in consensus validation while earning transaction fees and block rewards.
References & Further Reading for Solana (SOL)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Authoritative Media / Research:
Related Articles

The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges: Full-Chain Interoperability Becomes Inevitable, Liquidity Bridges Will Decline

Solana Need L2s And Appchains?
