What is Zcash?

What Is Zcash (ZEC)?
Zcash, known as "大零币" in Chinese and represented by the symbol ZEC, is the native cryptocurrency of a public blockchain that places a strong emphasis on transaction privacy. Utilizing zero-knowledge proofs, Zcash enables users to send verifiable transactions without revealing the sender, recipient, or transaction amount. It offers two types of address formats: transparent addresses and shielded addresses. Users can selectively disclose transaction details using a “viewing key,” supporting both privacy and compliance needs such as audits.
Zcash (ZEC) Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply
As of January 19, 2026, the reference data indicates: the price of ZEC is approximately $369.96; circulating supply is around 16,503,851.73 ZEC; total supply is about 16,505,342.35 ZEC; maximum supply is capped at 21 million; circulating market capitalization is roughly $6.106 billion; fully diluted market cap is also around $6.106 billion; market dominance is approximately 0.18%. Short-term performance: 1 hour -0.069%, 24 hours -7.27%, 7 days -8.20%, 30 days -18.16%.
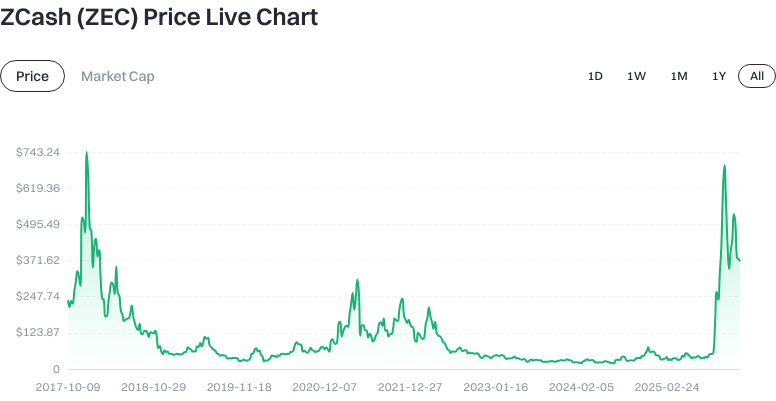
View the latest ZEC price data
The 24-hour trading volume is approximately $13.04 million. Market data fluctuates in real time; always refer to Gate’s live pricing page for the latest information.
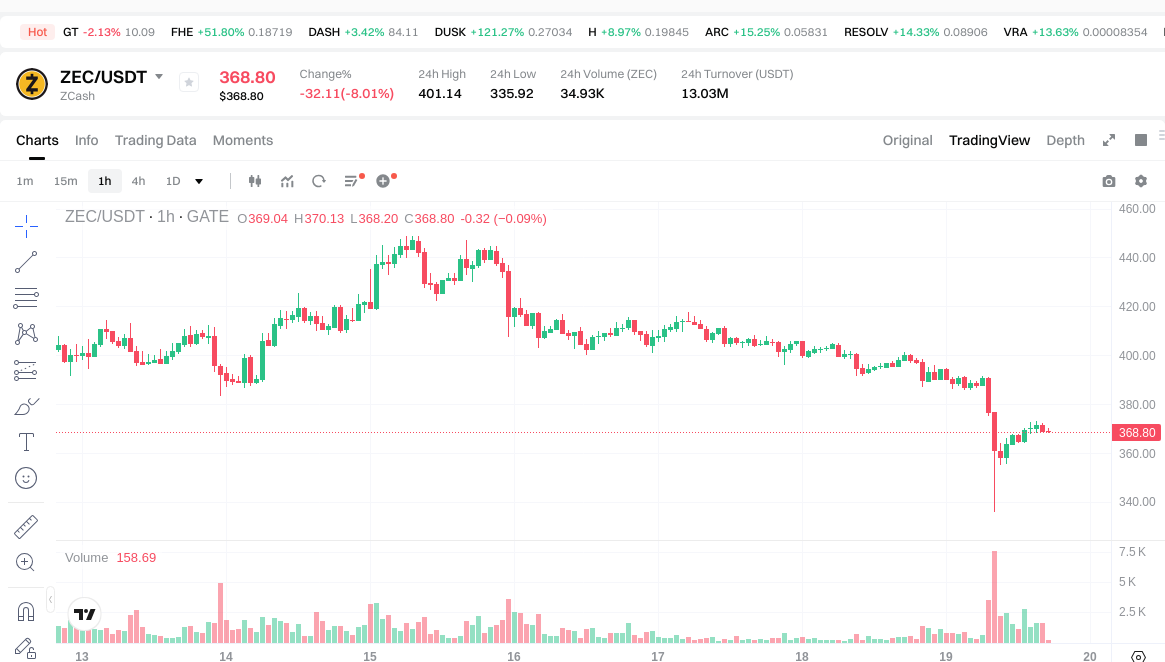
Check the ZEC/USDT price
Who Created Zcash (ZEC) and When?
Zcash was developed by Zooko Wilcox and the Electric Coin Company (ECC) team, launching its mainnet on October 27, 2016. The protocol is a fork from Bitcoin version 0.11.2, introducing zero-knowledge proofs at the privacy layer to enable shielded transactions. The early network included a reward mechanism to fund research and ecosystem support, which later evolved into a development fund managed by community governance to continuously sustain protocol and ecosystem growth.
How Does Zcash (ZEC) Work?
The core of Zcash is zero-knowledge proofs—a cryptographic technique that allows one party to prove a statement is true without revealing specific details. Zcash implements zk-SNARKs and subsequent upgrades, enabling on-chain nodes to verify shielded transactions without seeing addresses or amounts.
Zcash supports two address types: transparent addresses (t-addresses) and shielded addresses (z-addresses). Transactions sent from transparent addresses are visible on-chain, similar to Bitcoin. Shielded address transactions are encrypted, with details accessible only via a “viewing key” for selective disclosure. This model protects user privacy while providing interfaces for corporate audit and compliance.
At the consensus layer, Zcash uses Proof of Work (PoW) with mining to produce blocks and confirm transactions. Historically, it employed the Equihash algorithm to encourage broad mining participation. ZEC has a maximum supply of 21 million coins, with issuance and halving schedules similar to Bitcoin to control inflation and dilution.
What Are the Use Cases for Zcash (ZEC)?
ZEC enables privacy-preserving payments for individuals who want to transfer funds on a public blockchain without exposing recipient addresses or amounts. Enterprises can use ZEC for payments and procurement while disclosing required details to auditors via viewing keys without making them public. Other scenarios include cross-border donations, payroll distribution, and settlement of sensitive business transactions using shielded addresses to minimize the risk of information leakage.
Zcash (ZEC) Wallets and Ecosystem Solutions
The Zcash ecosystem includes both full-node wallets and lightweight wallets. Full-node wallets (which store the entire blockchain) are suitable for developers and users requiring high trust guarantees. Lightweight wallets simplify synchronization and proofs, making them more user-friendly on mobile devices. Some hardware wallets have mature support for transparent addresses, while shielded address support depends on ongoing ecosystem development—always verify wallet compatibility with z-addresses and viewing key export before use. Key features include mnemonic generation, private and viewing key backup, asset migration between t/z addresses, and selective transaction history disclosure.
Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Zcash (ZEC)
Privacy & Compliance: Some jurisdictions impose stricter regulations on privacy coins like Zcash, potentially affecting listings, trading, and reporting obligations. Always comply with local laws and securely retain viewing keys for potential audits.
Technical & Wallet Support: Shielded addresses require cryptographic proofs and client compatibility; wallet support may vary. Before use, confirm wallet version and backup mnemonics and viewing keys to avoid asset loss due to device failure.
Market & Liquidity: Crypto assets are highly volatile; liquidity impacts order execution slippage. Using split orders and limit orders can help manage execution risks.
Protocol & Security: Complex cryptographic systems may carry implementation risks or uncertainties during upgrades—monitor official channels and community updates for protocol changes and security advisories.
How to Buy and Securely Store Zcash (ZEC) on Gate
Step 1: Register an account on Gate and enable two-factor authentication. Visit the official website to register via email or phone, set a strong password, and activate two-factor authentication for enhanced account security.
Step 2: Complete identity verification (KYC) and risk assessment as prompted on the platform, reviewing trading and risk disclosures.
Step 3: Deposit or buy USDT. You can purchase USDT via fiat channels or transfer USDT from personal wallets/other platforms into your Gate account as preparation for trading ZEC.
Step 4: Search for ZEC in the spot market and place your order. Go to Gate’s spot section, search “ZEC/USDT,” select a limit or market order according to your needs, confirm quantity and price, then submit your order.
Step 5: Withdraw and securely store your ZEC. For self-custody, withdraw funds to a compatible ZEC wallet. To use privacy features, choose wallets supporting shielded addresses (z-addresses), generate and securely back up mnemonics and viewing keys, verify a small test transaction before transferring larger amounts.
Step 6: Ongoing security management. Keep offline backups of private keys and mnemonics, set anti-phishing codes, regularly check for wallet updates; when audit is needed, only disclose necessary information using viewing keys to compliant parties.
How Does Zcash (ZEC) Compare to Bitcoin?
Privacy Model: Bitcoin uses public but pseudonymous addresses—transaction details are visible to anyone on-chain. Zcash uses zero-knowledge proofs with shielded addresses to hide sender/receiver identities and amounts, allowing selective disclosure via viewing keys.
Supply & Issuance: Both have a maximum supply of 21 million coins with halving schedules. Zcash initially used block rewards to fund development and the ecosystem, later evolving into a development fund—Bitcoin does not have this mechanism.
Technical Architecture: Both use Proof of Work consensus on public blockchains; however, Zcash adds privacy components like zero-knowledge proofs and shielded pools that require nodes to validate additional cryptographic proofs.
Compliance & Use Cases: Bitcoin is widely adopted as an asset class and store of value; Zcash suits scenarios where counterparties or amounts need privacy while maintaining auditability. Its strong privacy features subject it to stricter regulatory scrutiny in some regions.
Summary of Zcash (ZEC)
Zcash combines zero-knowledge proofs with verifiability to enable “auditable but not public” transfers on a transparent blockchain. As of January 19, 2026 data, ZEC has a limited supply with market cap and trading volume placing it among medium-to-large crypto assets. Users benefit from both transparent and shielded address options; viewing keys allow individuals or businesses to balance privacy with compliance requirements. In practice, it’s recommended to start with small trades on Gate to become familiar with trading and withdrawals, use wallets supporting z-addresses, back up mnemonics/viewing keys securely, monitor protocol upgrades/local regulations, diversify trades, and practice prudent risk management for safe usage and storage.
FAQ
How Does Zcash Achieve Privacy?
Zcash uses zk-SNARK zero-knowledge proof technology to protect privacy by enabling transaction verification without revealing transaction details on-chain. This is Zcash’s core innovation compared to Bitcoin: sender, receiver, and amounts can all remain confidential. Users can choose between transparent or shielded addresses depending on their privacy needs or compliance requirements.
Why Is Zcash More Private Than Bitcoin?
All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger—while addresses are pseudonymous rather than real names, transaction chains can be traced. Zcash supports fully private “shielded transactions,” hiding sender/receiver identities and amounts from public view—making it a true privacy coin suited for users with high privacy demands but subjecting it to heightened regulatory scrutiny.
What Risks Should I Consider When Holding Zcash?
Because of its privacy features, some exchanges or countries restrict Zcash trading—check local legal status before purchasing. Use secure wallets (like the official Ywallet or hardware wallets) to prevent private key exposure. Be aware of possible technical vulnerabilities affecting privacy functions and monitor regulatory changes that may impact pricing.
Which Major Wallets Support Zcash?
Zcash supports multiple wallets including the official Ywallet (mobile), Zecwallet (desktop), Ledger and Trezor hardware wallets, as well as exchange wallets like Gate’s. Beginners are advised to start trading within Gate; for long-term holding, choose hardware wallets for maximum security—never share your private key with anyone.
How Should Regular Investors View Zcash’s Investment Value?
Zcash derives value from its unique privacy technology and legitimate privacy use cases (such as protecting commercial secrets). However, privacy coins face substantial regulatory risks—some countries or exchanges may restrict trading rights. Investors should rationally assess regulatory risks associated with privacy coins; it is not recommended as a primary investment but may be considered for small portfolio allocation to experience privacy coin technology.
Glossary of Key Zcash (ZEC) Terms
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: A cryptographic method that proves a statement is true without revealing specific information—the foundation of Zcash’s privacy.
- Privacy Transaction: A transaction model using zero-knowledge proofs to conceal sender, receiver, and amount details.
- Transparent Address: A public address type similar to Bitcoin where transaction details are visible; optional for Zcash users.
- Shielded Address: A unique private address type in Zcash leveraging zero-knowledge proofs to hide transaction data.
- Proof of Work: The consensus mechanism used by Zcash where computational effort validates transactions and secures the network.
- Equihash Algorithm: The PoW mining algorithm used by Zcash designed to resist ASIC specialization.
Further Reading & Official Resources on Zcash (ZEC)
-
Official Website/Whitepaper:
-
Development/Documentation:
-
Authoritative Media & Research:
Related Articles

How zk-SNARK Improves Gate.com's Proof of Reserves
A Detailed Explanation of Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKP)
